Breadcrumb
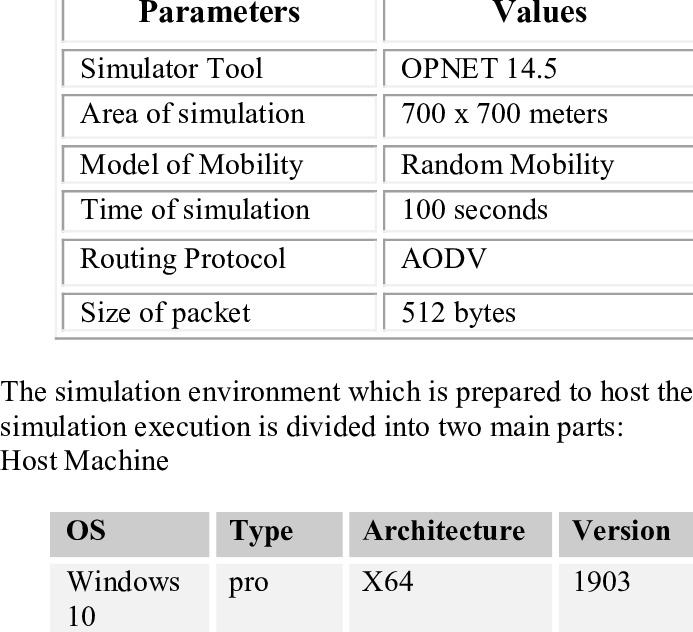
Blackhole Attack effect on MANETs' Performance
Mobile Ad hoc networks (MANETs) facilitate the communication of devices with a limited communication range. A MANET can be described as a decentralized network with a constantly changing topology. This makes it vulnerable to different attacks. The black hole is one of the most dangerous attacks in MANETs. This paper discusses the Blackhole attack in a random mobility environment and analyses its impact on MANETs using several parameters for single and multiple connections. © 2022 IEEE.
On The Arabic Dialects' Identification: Overcoming Challenges of Geographical Similarities Between Arabic dialects and Imbalanced Datasets
Arabic is one of the world's richest languages, with a diverse range of dialects based on geographical origin. In this paper, we present a solution to tackle subtask 1 (Country-level dialect identification) of the Nuanced Arabic Dialect Identification (NADI) shared task 2022 achieving third place with an average macro F1 score between the two test sets of 26.44%. In the preprocessing stage, we removed the most common frequent terms from all sentences across all dialects, and in the modeling step, we employed a hybrid loss function approach that includes Weighted cross entropy loss and Vector
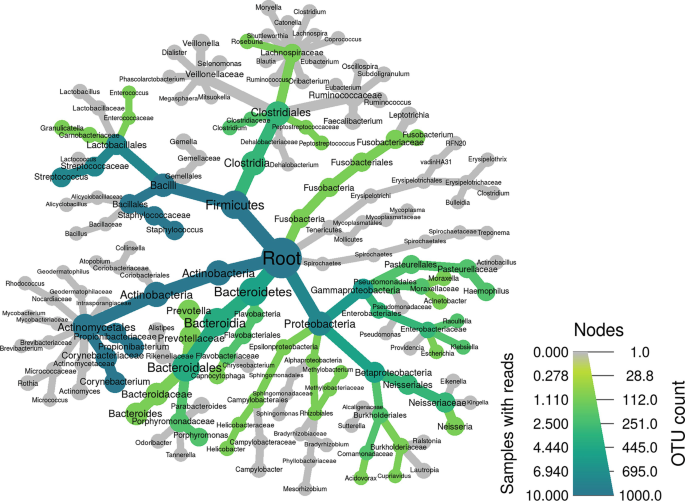
Comprehensive Guideline for Microbiome Analysis Using R
The need for a comprehensive consolidated guide for R packages and tools that are used in microbiome data analysis is significant; thus, we aim to provide a detailed step-by-step dissection of the most used R packages and tools in the field of microbiome data integration and analysis. The guideline aims to be a user-friendly simplification and tutorial on five main packages, namely phyloseq, MegaR, DADA2, Metacoder, and microbiomeExplorer due to their high efficiency and benefit in microbiome data analysis. © 2023, The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
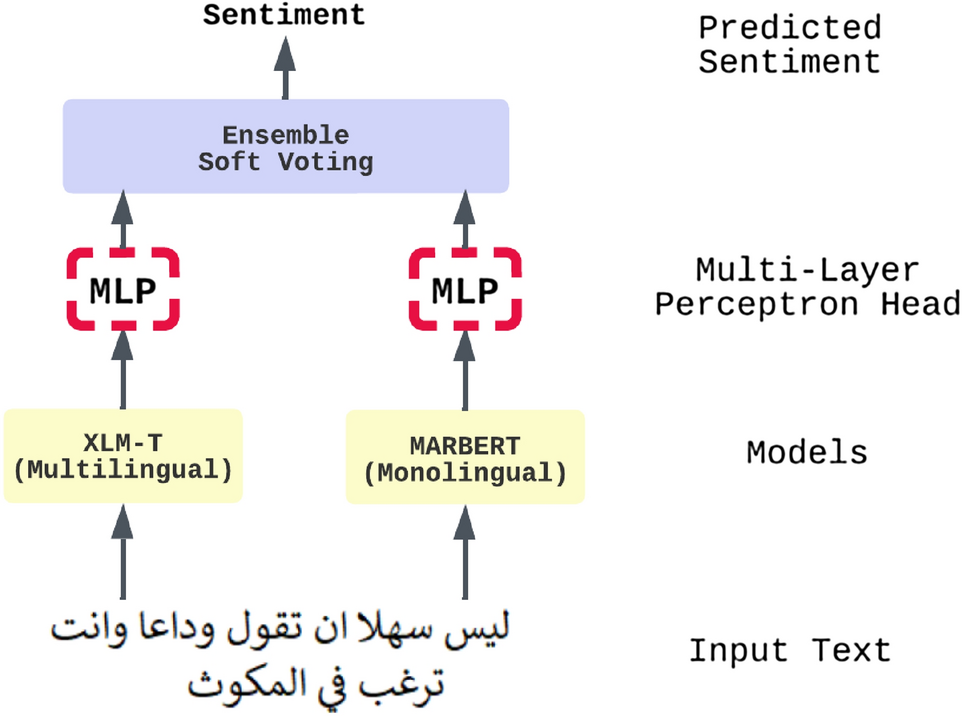
An ensemble transformer-based model for Arabic sentiment analysis
Sentiment analysis is a common and challenging task in natural language processing (NLP). It is a widely studied area of research; it facilitates capturing public opinions about a topic, product, or service. There is much research that tackles English sentiment analysis. However, the research in the Arabic language is behind other high-resource languages. Recently, models such as bidirectional encoder representations from transformers (BERT) and generative pre-trained transformer (GPT) have been widely used in many NLP tasks; it significantly improved performance in NLP tasks, especially
ArabicQuest: Enhancing Arabic Visual Question Answering with LLM Fine-Tuning
In an attempt to bridge the semantic gap between language understanding and visuals, Visual Question Answering (VQA) offers a challenging intersection of computer vision and natural language processing. Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown remarkable ability in natural language understanding; however, their use in VQA, particularly for Arabic, is still largely unexplored. This study aims to bridge this gap by examining how well LLMs can improve VQA models. We use state-of-the-art AI algorithms on datasets from multiple fields, including electric devices, Visual Genome, RSVQA, and ChartsQA

Anomaly Detection Based on CNN and Regularization Techniques Against Zero-Day Attacks in IoT Networks
The fast expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT) in the technology and communication industries necessitates a continuously updated cyber-security mechanism to keep protecting the systems' users from any possible attack that might target their data and privacy. Botnets pose a severe risk to the IoT, they use malicious nodes in order to compromise other nodes inside the network to launch several types of attacks causing service disruption. Examples of these attacks are Denial of Service (DoS), Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS), Service Scan, and OS Fingerprint. DoS and DDoS attacks are the
In-Silico targeting of SARS-CoV-2 NSP6 for drug and natural products repurposing
Non-Structural Protein 6 (NSP6) has a protecting role for SARS-CoV-2 replication by inhibiting the expansion of autophagosomes inside the cell. NSP6 is involved in the endoplasmic reticulum stress response by binding to Sigma receptor 1 (SR1). Nevertheless, NSP6 crystal structure is not solved yet. Therefore, NSP6 is considered a challenging target in Structure-Based Drug Discovery. Herein, we utilized the high quality NSP6 model built by AlphaFold in our study. Targeting a putative NSP6 binding site is believed to inhibit the SR1-NSP6 protein-protein interactions. Three databases were
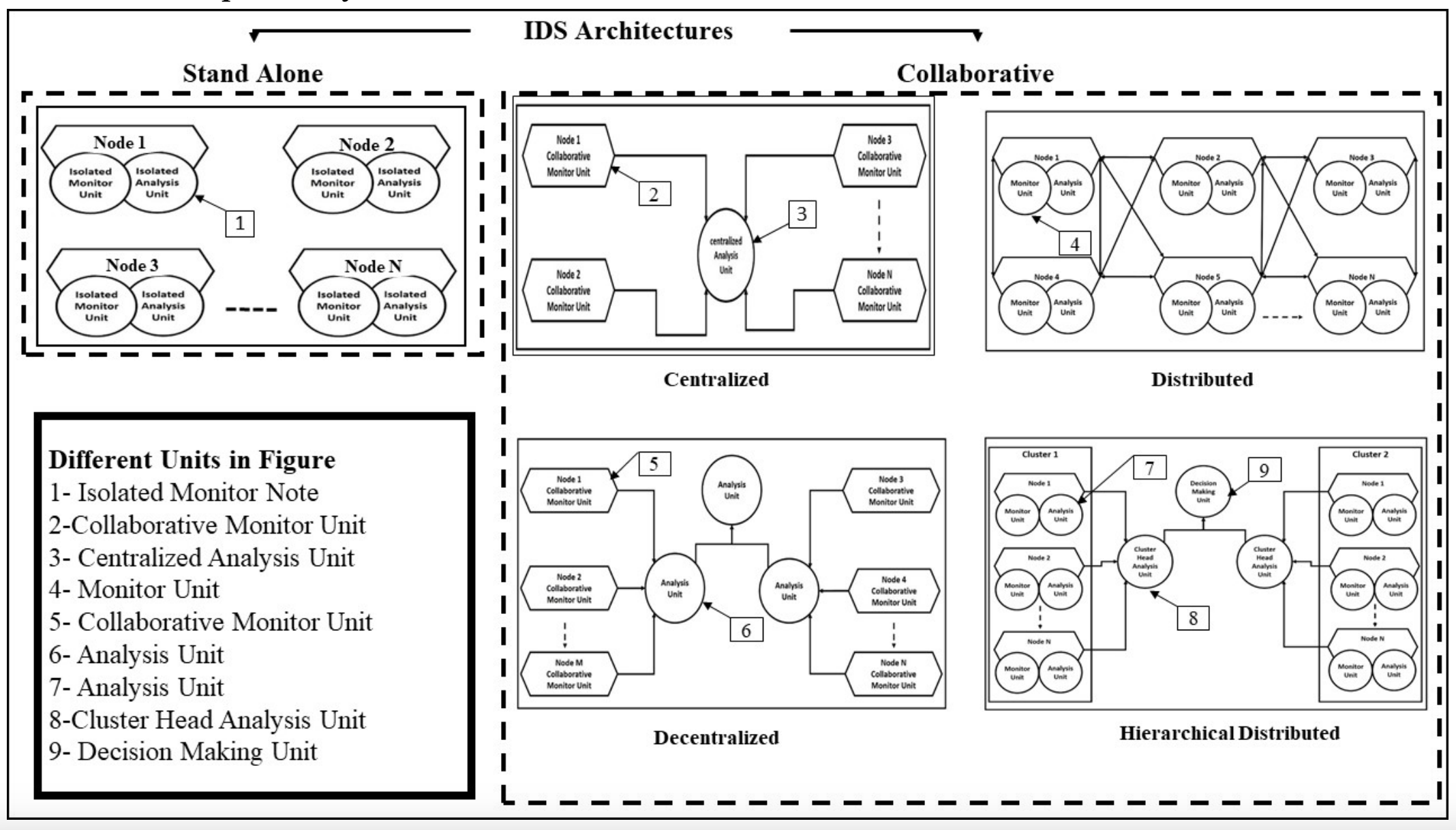
MSDAR: Multi-Stage Dynamic Architecture Intrusion Detection System
Ad hoc networks have been through extensive research in the last decade. Even with their desirable characteristics, major issues related to their security need to be considered. Various security solutions have been proposed to reduce the risks of malicious actions. They mainly focus on key management, authentication, secure localization, and aggregation techniques. These techniques have been proposed to secure wireless communications but they can only deal with external threats. Therefore, they are considered the first line of defense. Intrusion detection systems are always required to
Towards Arabic Image Captioning: A Transformer-Based Approach
The automatic generation of textual descriptions from images, known as image captioning, holds significant importance in various applications. Image captioning applications include accessibility for the visually impaired, social media enhancement, automatic image description for search engines, assistive technology for education, and many more. While extensive research has been conducted in English, exploring this challenge in Arabic remains limited due to its complexity. Arabic is one of the world's most widely spoken languages. Around 420 million native people speak this language. It is also

Sudden Fall Detection and Prediction Using AI Techniques
Fall prediction is a critical process in ensuring the safety and well-being of individuals, particularly the elderly population. This paper focuses on the development of a fall detection and prediction system using wearable sensors and machine learning algorithms. The system issues an alarm upon predicting the occurrence of falling and sends alerts to a monitoring centre for timely assistance. Wearable sensor devices, including Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs) equipped with accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers are utilized for data collection. UPFALL, a comprehensive online freely
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 3
- Next page ››
