Breadcrumb
Clay chips and beads capture in situ barley root microbiota and facilitate in vitro long-term preservation of microbial strains
Capturing the diverse microbiota from healthy and/or stress resilient plants for further preservation and transfer to unproductive and pathogen overloaded soils, might be a tool to restore disturbed plant-microbe interactions. Here, we introduce Aswan Pink Clay as a low-cost technology for capturing and storing the living root microbiota. Clay chips were incorporated into the growth milieu of barley plants and developed under gnotobiotic conditions, to capture and host the rhizospheric microbiota. Afterward, it was tested by both a culture-independent (16S rRNA gene metabarcoding) and
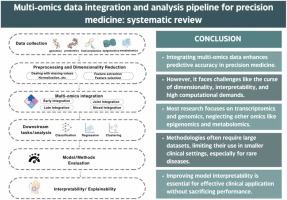
Multi-omics data integration and analysis pipeline for precision medicine: Systematic review
Precision medicine has gained considerable popularity since the “one-size-fits-all” approach did not seem very effective or reflective of the complexity of the human body. Subsequently, since single-omics does not reflect the complexity of the human body's inner workings, it did not result in the expected advancement in the medical field. Therefore, the multi-omics approach has emerged. The multi-omics approach involves integrating data from different omics technologies, such as DNA sequencing, RNA sequencing, mass spectrometry, and others, using computational methods and then analyzing the
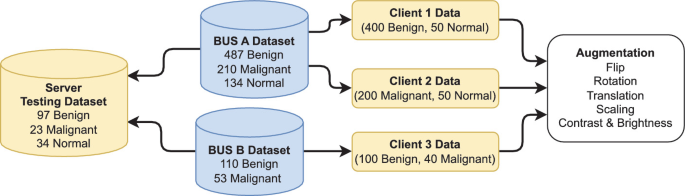
A Novel Approach to Breast Cancer Segmentation Using U-Net Model with Attention Mechanisms and FedProx
Breast cancer is a leading cause of death among women worldwide, emphasizing the need for early detection and accurate diagnosis. As such Ultrasound Imaging, a reliable and cost-effective tool, is used for this purpose, however the sensitive nature of medical data makes it challenging to develop accurate and private artificial intelligence models. A solution is Federated Learning as it is a promising technique for distributed machine learning on sensitive medical data while preserving patient privacy. However, training on non-Independent and non-Identically Distributed (non-IID) local datasets
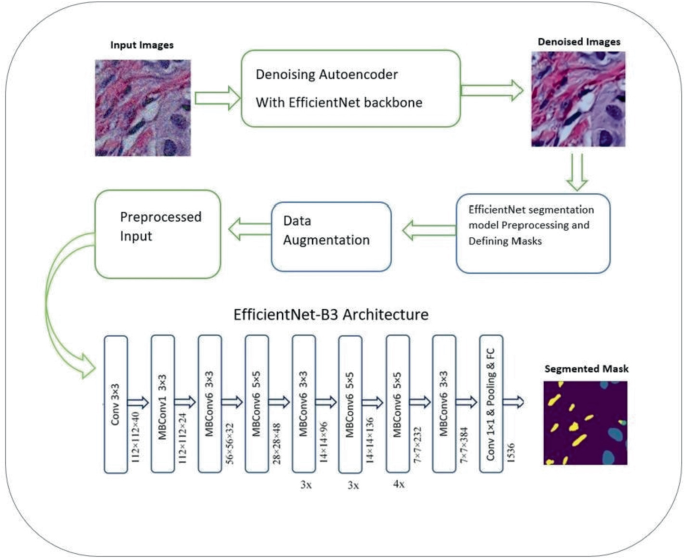
Revolutionizing Cancer Diagnosis Through Hybrid Self-supervised Deep Learning: EfficientNet with Denoising Autoencoder for Semantic Segmentation of Histopathological Images
Machine Learning technologies are being developed day after day, especially in the medical field. New approaches, algorithms and architectures are implemented to increase the efficiency and accuracy of diagnosis and segmentation. Deep learning approaches have proven their efficiency; these approaches include architectures like EfficientNet and Denoising Autoencoder. Accurate segmentation of nuclei in histopathological images is essential for the diagnosis and prognosis of diseases like cancer. In this paper, we propose a novel method for semantic segmentation of nuclei using EfficientNet and
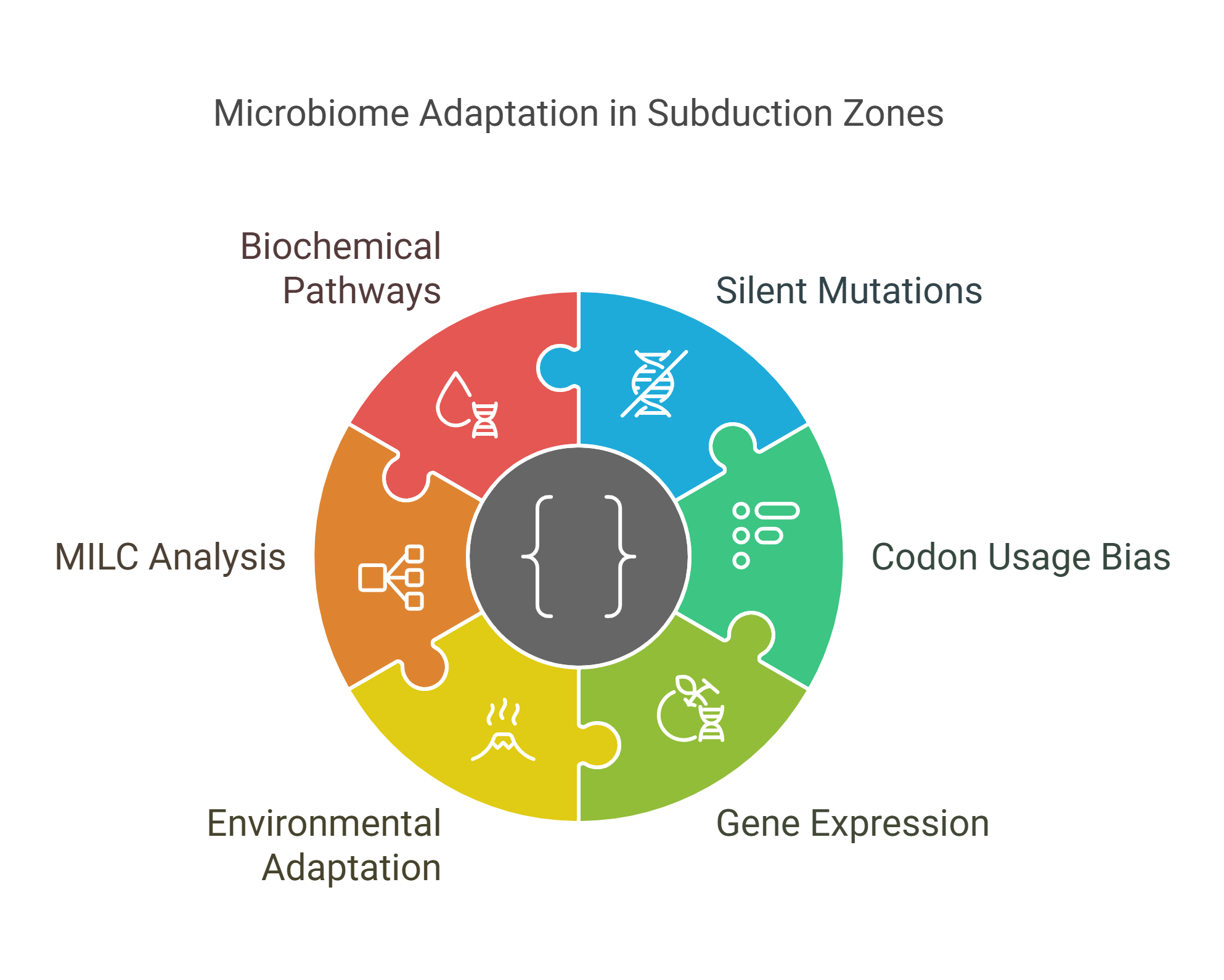
The Melody of Silent Mutations: Microbiome Adaptation Across the Subduction Zone
Silent mutations generate synonymous codons that encode the same amino acid however, they may be silent yet operative. These synonymous codons are used in unequal frequencies resulting in a phenomenon known as codon usage bias (CUB). It drives gene expression towards highly expressed and adaptation genes. In this study we investigated CUB in one of the largest, most dynamic exotic niches, the volcanic subduction zones in Costa Rica. CUB analysis in such challengingly inaccessible sites can help distinguish highly expressed genes under certain environmental factors, elucidating molecular

Uni-Buddy: A Multifunctional AI-Powered Assistant for Enhancing University Life: A Use Case at Nile University
Uni-Buddy is an advanced AI system developed to simplify university life at Nile University. It efficiently handles questions in everyday language, accesses real-time university databases, and simultaneously provides accurate responses for multiple users. Its goals include assisting with course registration, academic advising, financial inquiries, campus navigation, and research support. The evaluation demonstrates Uni-Buddy's user-friendly design, effective navigation, language comprehension, and database connectivity proficiency. Compared to similar studies, it stands out for its ease of use
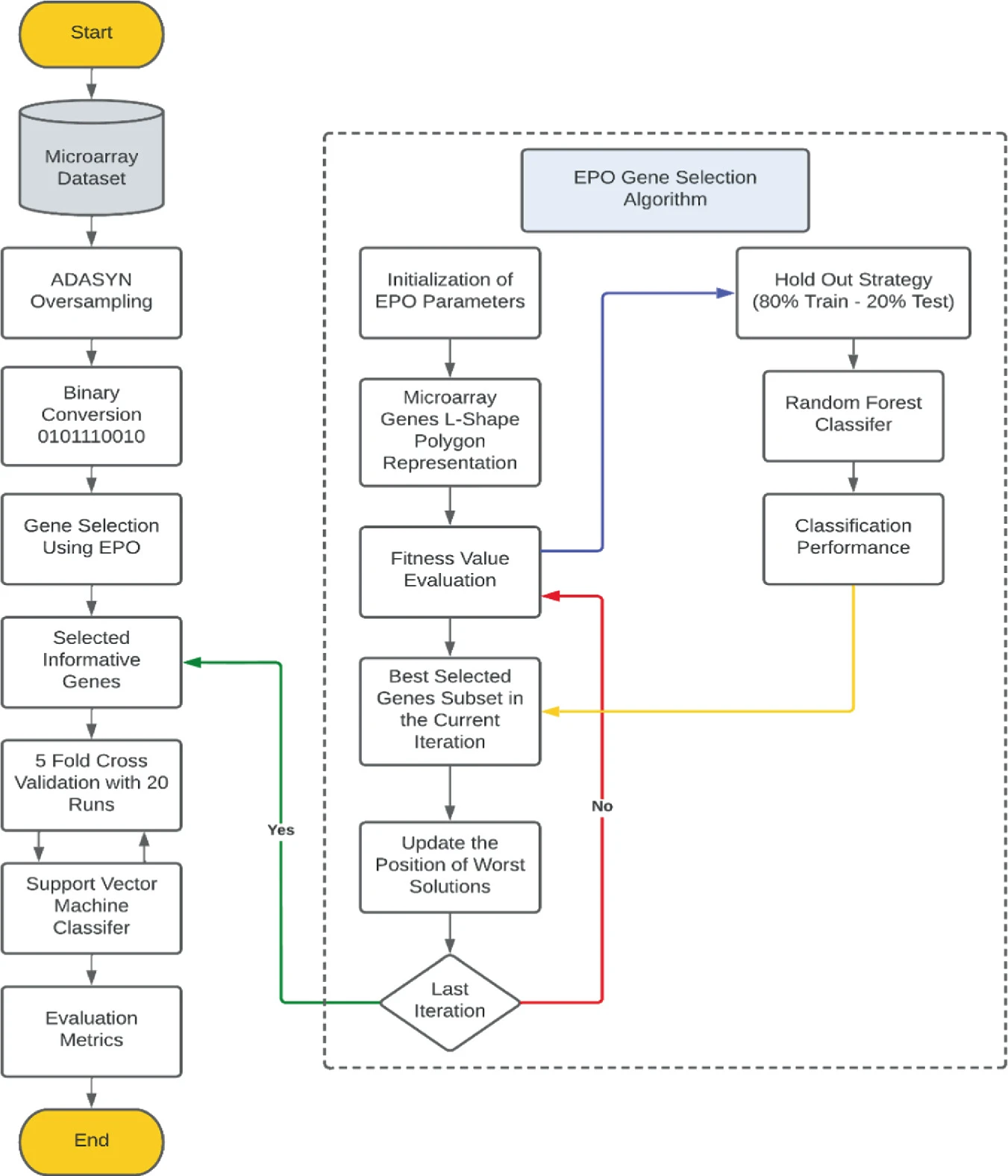
Computational Microarray Gene Selection Model Using Metaheuristic Optimization Algorithm for Imbalanced Microarrays Based on Bagging and Boosting Techniques
Genomic microarray databases encompass complex high dimensional gene expression samples. Imbalanced microarray datasets refer to uneven distribution of genomic samples among different contributed classes which can negatively affect the classification performance. Therefore, gene selection from imbalanced microarray dataset can give rise to misleading, and inconsistent nominated genes that would alter the classification performance. Such unsatisfactory classification performance is due to the skewed distribution of the samples across the microarrays toward the majority class. In this paper, we
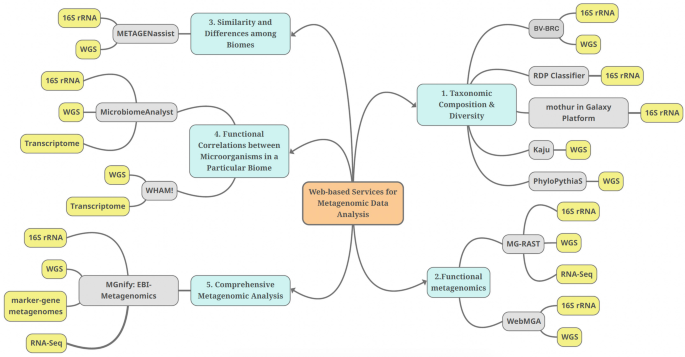
Interactive Web-Based Services for Metagenomic Data Analysis and Comparisons
Recently, sequencing technologies have become readily available, and scientists are more motivated to conduct metagenomic research to unveil the potential of a myriad of ecosystems and biomes. Metagenomics studies the composition and functions of microbial communities and paves the way to multiple applications in medicine, industry, and ecology. Nonetheless, the immense amount of sequencing data of metagenomics research and the few user-friendly analysis tools and pipelines carry a new challenge to the data analysis. Web-based bioinformatics tools are now being developed to facilitate the
Genomic image representation of human coronavirus sequences for COVID-19 detection
Coronavirus (CoV) disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a severe pandemic affecting millions worldwide. Due to its rapid evolution, researchers have been working on developing diagnostic approaches to suppress its spread. This study presents an effective automated approach based on genomic image processing (GIP) techniques to rapidly detect COVID-19, among other human CoV diseases, with high acceptable accuracy. The GIP technique was applied as follows: first, genomic graphical mapping techniques were used to convert the genome sequences into genomic grayscale images. The frequency chaos game
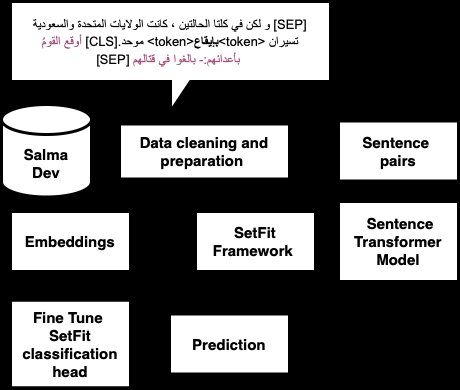
Pirates at ArabicNLU2024: Enhancing Arabic Word Sense Disambiguation using Transformer-Based Approaches
This paper presents a novel approach to Arabic Word Sense Disambiguation (WSD) leveraging transformer-based models to tackle the complexities of the Arabic language. Utilizing the SALMA dataset, we applied several techniques, including Sentence Transformers with Siamese networks and the SetFit framework optimized for few-shot learning. Our experiments, structured around a robust evaluation framework, achieved a promising F1-score of up to 71%, securing second place in the ArabicNLU 2024: The First Arabic Natural Language Understanding Shared Task competition. These results demonstrate the
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 4
- Next page ››
