Breadcrumb
Dual-Level Sensor Selection with Adaptive Sensor Recovery to Extend WSNs’ Lifetime
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) have garnered much attention in the last decades. Nowadays, the network contains sensors that have been expanded into a more extensive network than the internet. Cost is one of the issues of WSNs, and this cost may be in the form of bandwidth, computational cost, deployment cost, or sensors’ battery (sensor life). This paper proposes a dual-level sensor selection (DLSS) model used to reduce the number of sensors forming WSNs. The sensor reduction process is performed at two consecutive levels. First, a combination of the Fisher score method and ANOVA test at the
Rough Sets Hybridization with Mayfly Optimization for Dimensionality Reduction
Big data is a vast amount of structured and unstructured data that must be dealt with on a regular basis. Dimensionality reduction is the process of converting a huge set of data into data with tiny dimensions so that equal information may be expressed easily. These tactics are frequently utilized to improve classification or regression challenges while dealing with machine learning issues. To achieve dimensionality reduction for huge data sets, this paper offers a hybrid particle swarm optimization-rough set PSO-RS and Mayfly algorithm-rough set MA-RS. A novel hybrid strategy based on the
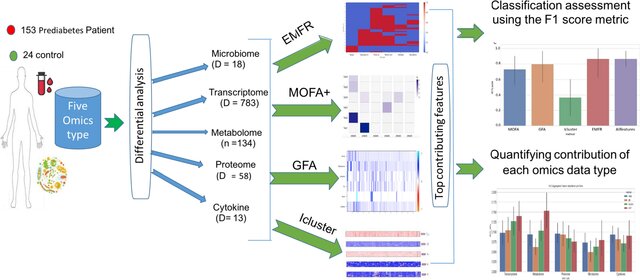
Comparative evaluation of multiomics integration tools for the study of prediabetes: insights into the earliest stages of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D) remains a critical health concern, particularly in its early disease stages such as prediabetes. Understanding these early stages is paramount for improving patient outcomes. Multiomics data integration tools offer promise in unraveling the underlying mechanisms of T2D. The advent of high-throughput technology and the increasing availability of multiomics data has led to the development of several statistical and network-based integration methods. However, the performance of such methods varies, requiring their output evaluation in an unbiased manner. Here, we
Hybrid Global Optimization Algorithm for Feature Selection
This paper proposes Parallelized Linear Time-Variant Acceleration Coefficients and Inertial Weight of Particle Swarm Optimization algorithm (PLTVACIW-PSO). Its designed has introduced the benefits of Parallel computing into the combined power of TVAC (Time-Variant Acceleration Coefficients) and IW (Inertial Weight). Proposed algorithm has been tested against linear, non-linear, traditional, and multiswarm based optimization algorithms. An experimental study is performed in two stages to assess the proposed PLTVACIW-PSO. Phase I uses 12 recognized Standard Benchmarks methods to evaluate the
Malware Detection Techniques
Computers and systems are vulnerable to many threats. Security researchers identified the malware as the major computers and systems threat. Malware can be classified into different types depending on the infection, attacking target, and persistence technique. In this paper, Malware detection techniques are observed with the identification of each technique's strengths and weaknesses points, followed by a comparison between all malware detection techniques. © 2022 IEEE.
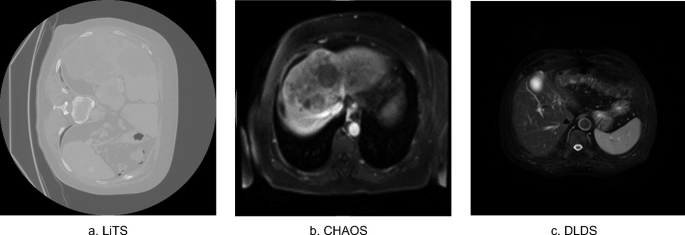
Cross-Modality Deep Transfer Learning: Application to Liver Segmentation in CT and MRI
Liver diseases cause up to two million deaths yearly. Their diagnosis and treatment plans require an accurate assessment of the liver structure and tissue characteristics. Imaging modalities such as computed tomography (CT) and Magnetic resonance (MR) can be used to assess the liver. CT has better spatial resolution compared to MR, which has better tissue contrast. Each modality has its own applications. However, CT is widely used due its ease of access, lower cost and a shorter examination time. Liver segmentation is an important step that helps to accurately identify and isolate the liver

ArFakeDetect: A Deep Learning Approach for Detecting Fabricated Arabic Tweets on COVID-19 Vaccines
Social media platforms have emerged as major sources of false information, particularly regarding health topics. like COVID-19 vaccines. This rampant dissemination of inaccurate content contributes significantly to vaccine hesitancy and undermines vaccination campaigns. This research addresses the pressing need for automated methods to distinguish between factual and fabricated Arabic tweets concerning vaccines, aiming to mitigate the spread of misinformation on these platforms. The proposed approach utilizes deep learning techniques, leveraging pre-trained Arabic language models (Arabert)
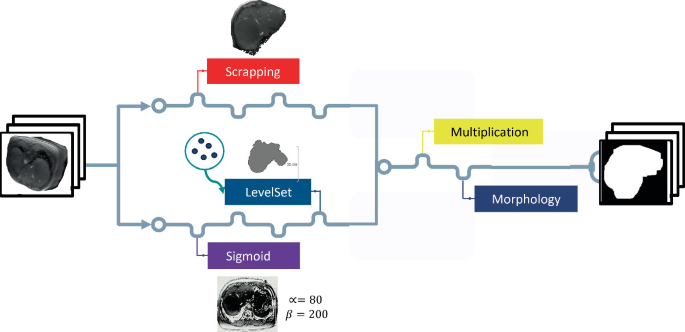
Iterative Refinement Algorithm for Liver Segmentation Ground-Truth Generation Using Fine-Tuning Weak Labels for CT and Structural MRI
Medical image segmentation is indicated in a number of treatments and procedures, such as detecting pathological changes and organ resection. However, it is a time-consuming process when done manually. Automatic segmentation algorithms like deep learning methods overcome this hurdle, but they are data-hungry and require expert ground-truth annotations, which is a limitation, particularly in medical datasets. On the other hand, unannotated medical datasets are easier to come by and can be used in several methods to learn ground-truth masks. In this paper, we aim to utilize across-modalities
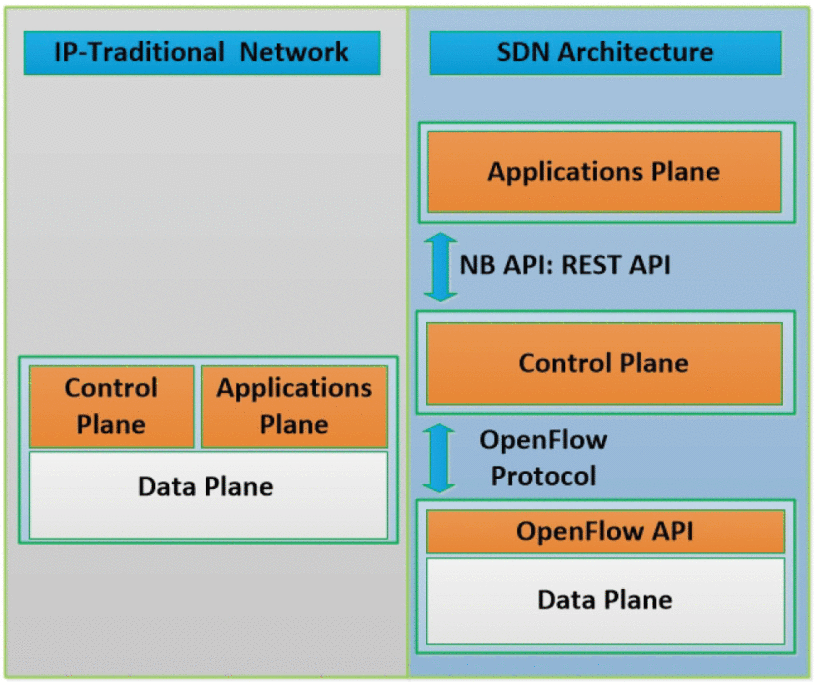
A Flow-Based Anomaly Detection Approach With Feature Selection Method Against DDoS Attacks in SDNs
Software Defined Networking (SDN) is an emerging network platform, which facilitates centralised network management. The SDN enables the network operators to manage the overall network consistently and holistically, regardless the complexity of infrastructure devices. The promising features of the SDN enhance network security and facilitate the implementation of threat detection systems through software applications using open APIs. However, the emerging technology creates new security concerns and new threats that do not exist in the current traditional networks. Distributed Denial of Service
Performance Comparison of AODV and DSDV in Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks
Vehicle Ad-Hoc Networks (VANETs) are a special type of Mobile Ad-Hoc Network (MANETs). In VANETs, a group of vehicles communicates with each other to transfer data without a need for a fixed infrastructure. In this paper, we compare the performance of two routing protocols: Ad-hoc on Demand Distance Vector protocol (AODV) and Destination-Sequenced Distance Vector protocol (DSDV) in VANETs. We measure the reliability of each protocol in the packet delivery. © 2022 IEEE.
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 2
- Next page ››
