Breadcrumb

Statistical Investigation of Scientific Journals Impact Factors in Relation to Benford's Law
Benford's law (BL) has been used as a tool for the detection of possible data manipulation in datasets. The statistics of the first digit(s) of the observed values are compared to a set of expected values given by BL, and violations signal possible data anomalies. Though this method is first used for economical purposes, it has been recently used in bibliometric statistical analyses. The method provides alert that records may have certain unusual trends. In the present work, we investigate the impact factor statistics for 24 years starting from 1997 up to 2021, for open access and subscribed

A (k,n)-Secret Image Sharing With Steganography Using Generalized Tent Map
Secret Image Sharing (SIS) transfers an image to mutually suspicious receivers as n meaningless shares, where k or more shares must be present to recover the secret. This paper proposes a (k, n)-SIS system for any image type using polynomial interpolation based on Lagrange polynomials, where the generated shares are of size 1/k of the secret image size. A full encryption system, consisting of substitution and permutation stages, is employed by using the generalized Tent map as a source of randomness. In addition to using a long and sensitive system key, steganography using the Least
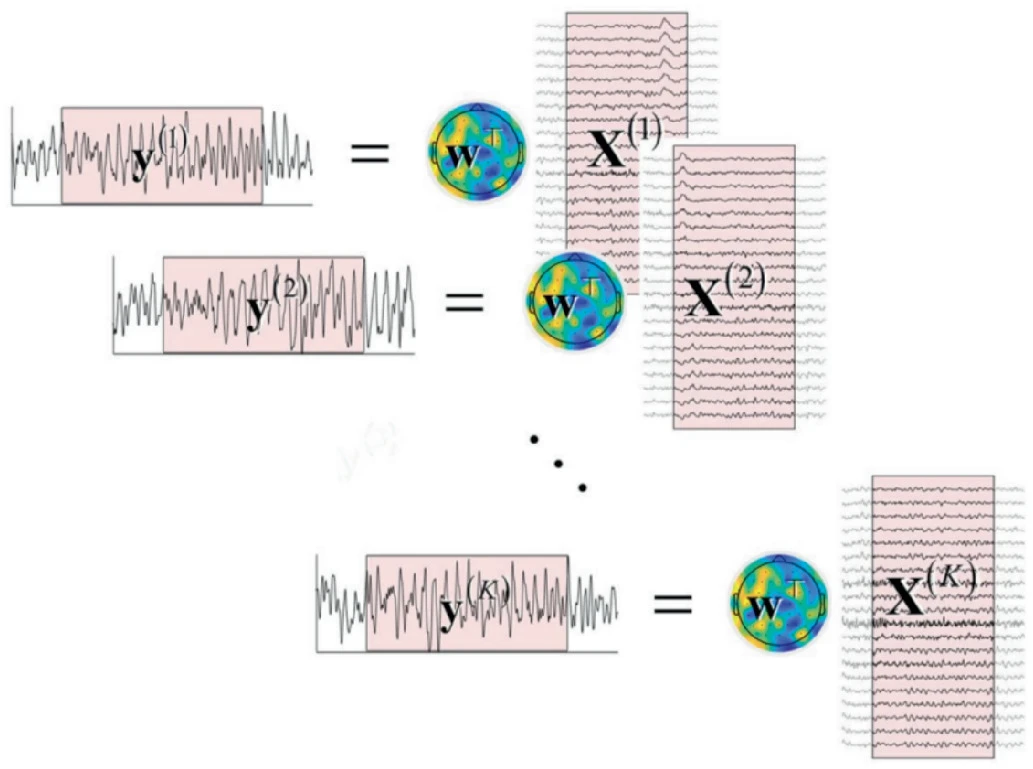
A Comparative Analysis of Time Series Transformers and Alternative Deep Learning Models for SSVEP Classification
Steady State Visually Evoked Potentials (SSVEPs) are intrinsic responses to specific visual stimulus frequencies. When the retina is activated by a frequency ranging from 3.5 to 75 Hz, the brain produces electrical activity at the same frequency as the visual signal, or its multiples. Identifying the preferred frequencies of neurocortical dynamic processes is a benefit of SSVEPs. However, the time consumed during calibration sessions limits the number of training trials and gives rise to visual fatigue since there is significant human variation across and within individuals over time, which

Semi-Fragile Watermark for the Authentication and Recovery of Tampered Images
In order to strengthen the safety of corporate multimedia assets, a semi-fragile watermarking method is developed, which makes use of the integer wavelet transform (IWT) and the discrete cosine transform (DCT) for tamper detection and recovery. In this paper, we produce two distinct kinds of watermarks: an authentication watermark and a recovery watermark. A tamper detection methodology is utilized at the receiving end to check the watermarked image for validity and detect any assaults. If the changes are determined to be malicious, the suggested tamper recovery method is used to restore the

Computational Intelligence for Medical Internet of Things (MIoT) Applications
Computational Intelligence for Medical Internet of Things (MIoT) Applications: Machine Intelligence Applications for IoT in Healthcare explores machine intelligence techniques necessary for effective MIoT research and practice, taking a practical approach for practitioners and students entering the field. This book investigates advanced concepts and applications in the MIoT field, guiding readers through emerging developments and future trends. A wide range of international authors guide readers through advanced concepts, including deep learning, neural network, and big data analytic
Influence of increasing amount of attapulgite on the performance properties of Cu-free brake-pads
Copper is almost inevitable functional filler in the brake-material and efforts to replace it are continuing since it is now known as a hazard to the aquatic life. It is always desirable to search for ingredients for Cu-free brake-pads, which will be beneficial for friction-related properties and especially fade resistance. Attapulgite, is a mineral which was proven to be an excellent substitute for asbestos in brake-pads long back. However, hardly anything in details is reported on its exact role in controlling tribo-properties of friction materials (FMs). It was of interest, if it can be
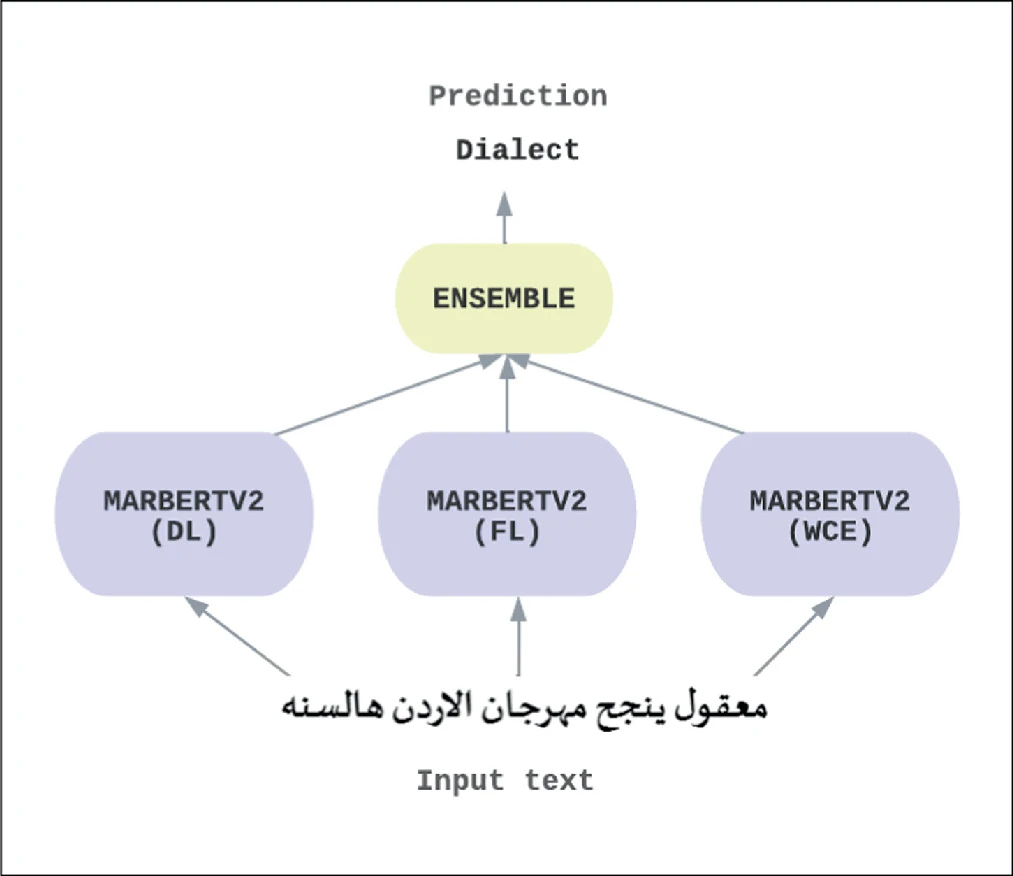
In the Identification of Arabic Dialects: A Loss Function Ensemble Learning Based-Approach
The automation of a system to accurately identify Arabic dialects many natural language processing tasks, including sentiment analysis, medical chatbots, Arabic speech recognition, machine translation, etc., will greatly benefit because it’s useful to understand the text’s dialect before performing different tasks to it. Different Arabic-speaking nations have adopted various dialects and writing systems. Most of the Arab countries understand modern standard Arabic (MSA), which is the native language of all other Arabic dialects. In this paper we propose a method for identifying Arabic dialects
NGU_CNLP at WANLP 2022 Shared Task: Propaganda Detection in Arabic
This paper presents the system developed by the NGU_CNLP team for addressing the shared task on Propaganda Detection in Arabic at WANLP 2022. The team participated in the shared tasks' two sub-tasks which are: 1) Propaganda technique identification in text and 2) Propaganda technique span identification. In the first sub-task the goal is to detect all employed propaganda techniques in some given piece of text out of a possible 17 different techniques, or to detect that no propaganda technique is being used in that piece of text. As such, this first sub task is a multi-label classification
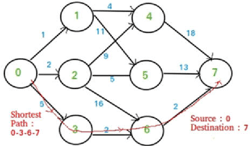
Comparison of Parallel and Serial Execution of Shortest Path Algorithms
Shortest Path Algorithms are an important set of algorithms in today's world. It has many applications like Traffic Consultation, Route Finding, and Network Design. It is essential for these applications to be fast and efficient as they mostly require real-Time execution. Sequential execution of shortest path algorithms for large graphs with many nodes is time-consuming. On the other hand, parallel execution can make these applications faster. In this paper, three popular shortest path algorithms-Dijkstra, Bellman-Ford, and Floyd Warshall-Are both implemented as serial and parallel programs
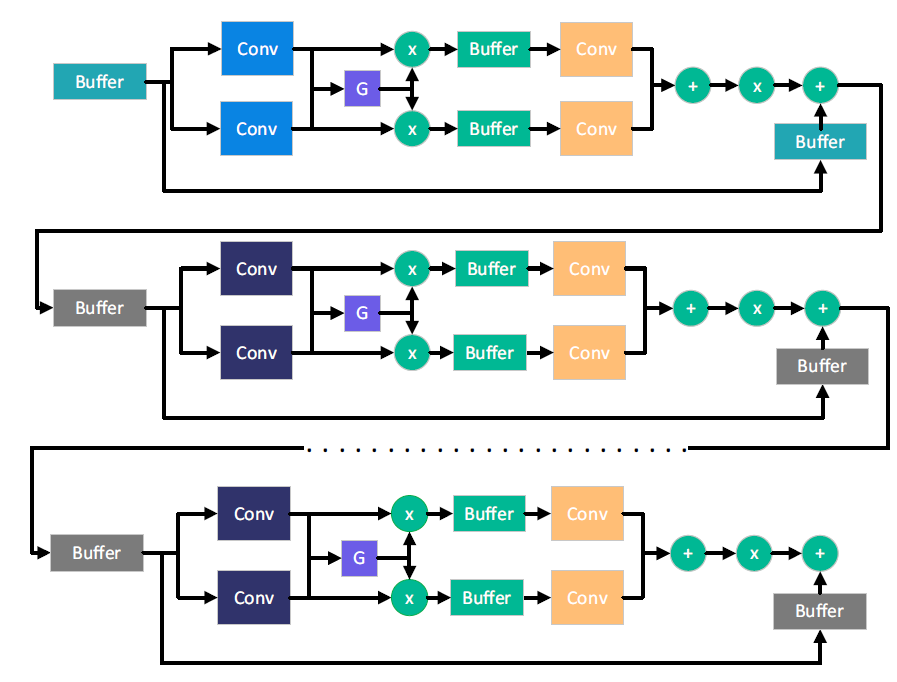
High-performance fractional anisotropic diffusion filter for portable applications
Anisotropic diffusion is one of the most effective methods used in image processing. It can be used to eliminate the small textures of an image while preserving its significant edges. In this paper, a new anisotropic diffusion filter is proposed based on a fractional calculus kernel rather than integer kernel to improve the overall performance of the filter. Integer and fractional anisotropic filters are implemented using the Genesys-2 FPGA kit to utilize the efficiency of parallelism in FPGAs. Integer and fractional anisotropic filters are tested against the achievable PSNR value vs the
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 15
- Next page ››
