Breadcrumb

Sentiment-Based Spatiotemporal Prediction Framework for Pandemic Outbreaks Awareness Using Social Networks Data Classification
According to the World Health Organization, several factors have affected the accurate reporting of SARS-CoV-2 outbreak status, such as limited data collection resources, cultural and educational diversity, and inconsistent outbreak reporting from different sectors. Driven by this challenging situation, this study investigates the potential expediency of using social network data to develop reliable early information surveillance and warning system for pandemic outbreaks. As such, an enhanced framework of three inherently interlinked subsystems is proposed. The first subsystem includes data
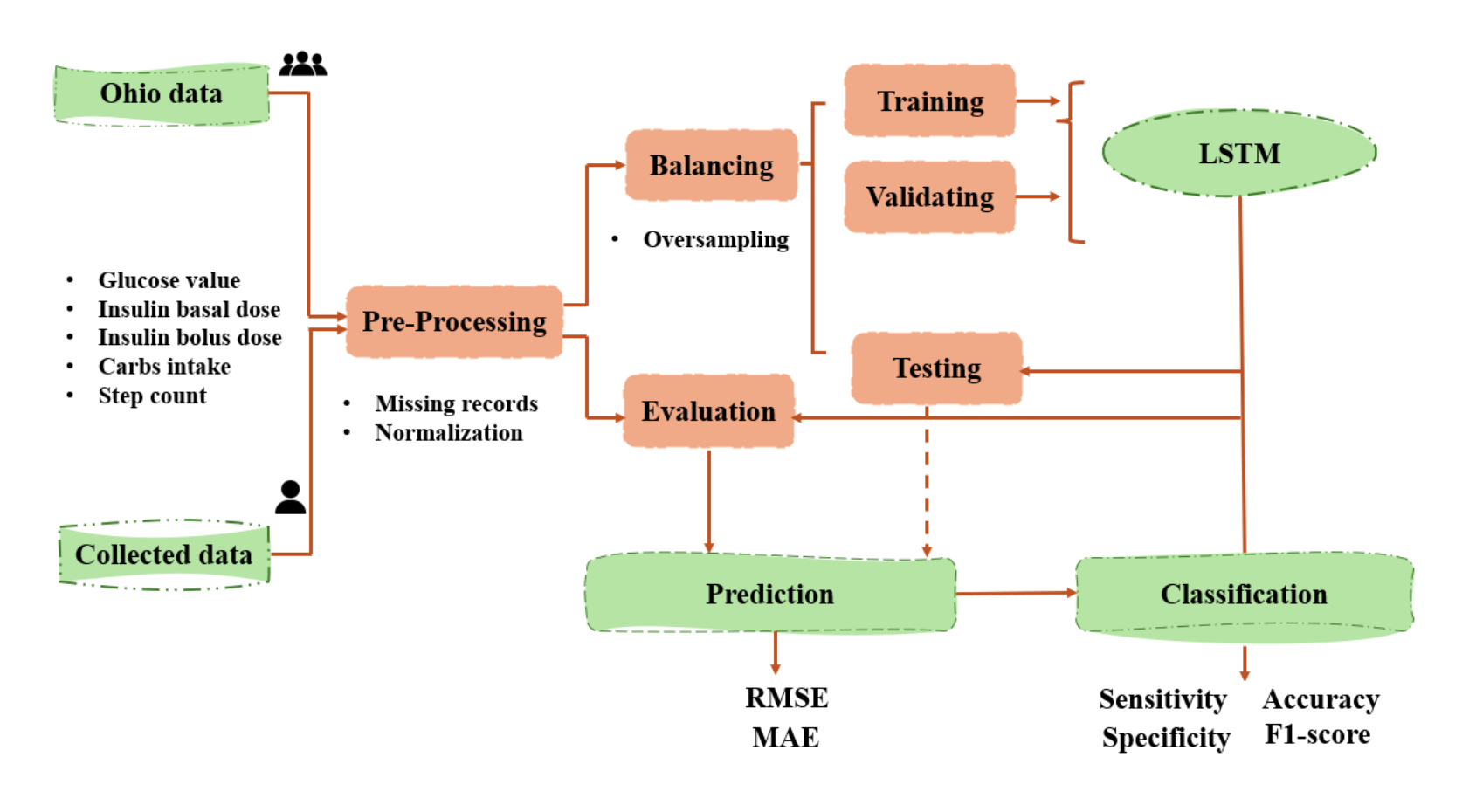
Intelligent Real-Time Hypoglycemia Prediction for Type 1 Diabetes
Hypoglycemia in Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) refers to a condition where blood glucose (BG) levels drop to abnormally low levels, typically below 70 mg/dL. This can occur when there is an excessive amount of insulin relative to the blood glucose level, leading to an imbalance that can be dangerous and potentially life-threatening if not promptly treated. The availability of large amounts of data from continuous glucose monitoring (CGM), insulin doses, carbohydrate intake, and additional vital signs, together with deep learning (DL) techniques, has revolutionized algorithmic approaches for BG
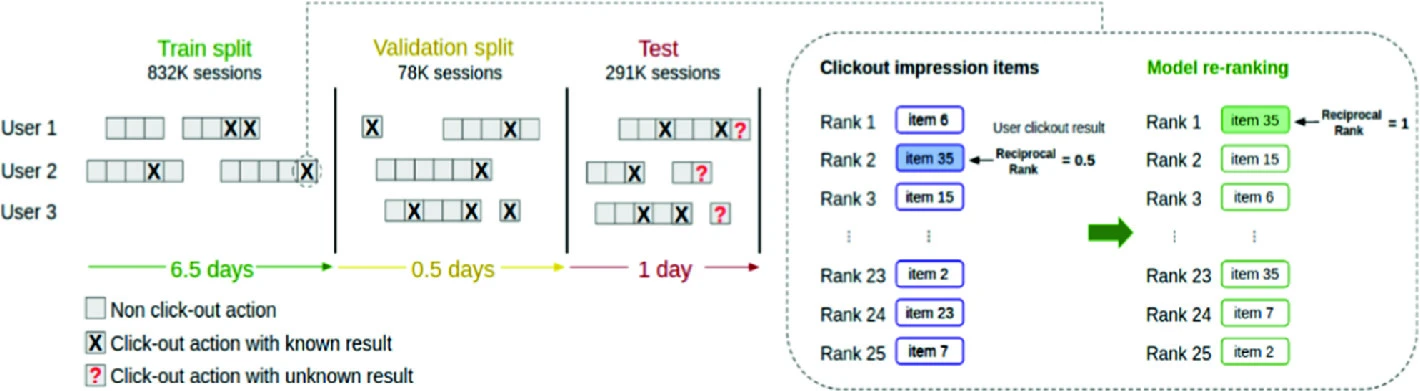
Recommendations on Streaming Data: E-Tourism Event Stream Processing Recommender System
The Association for Computing Machinery ACM recommendation systems challenge (ACM RecSys) [1] released an e-tourism dataset for the first time in 2019. Challenge shared hotel booking sessions from trivago website asking to rank the hotels list for the users. Better ranking should achieve higher click out rate. In this context, Trivago dataset is very important for e-tourism recommendation systems domain research and industry as well. In this paper, description for dataset characteristics and proposal for a session-based recommender system in addition to a comparison of several baseline
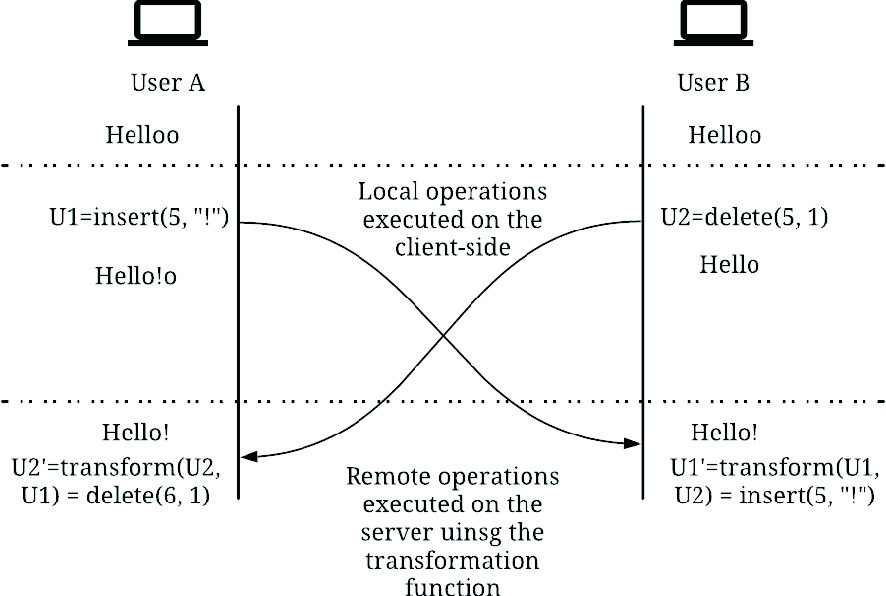
A Survey of Concurrency Control Algorithms in Collaborative Applications
Collaborative applications are becoming more prevalent for a variety of reasons, most important of which is the increased interest in remote work. In addition to adapting the business processes to a remote setting, designers of collaborative software have to decide on how their software can be used collaboratively. This paper discusses the two main technologies used to enable network-based real- or near-real-time collaborative software, namely Operational Transformation and Conflict-free Replicated Data Types. Recent developments in each technology are discussed, as well as a brief overview of
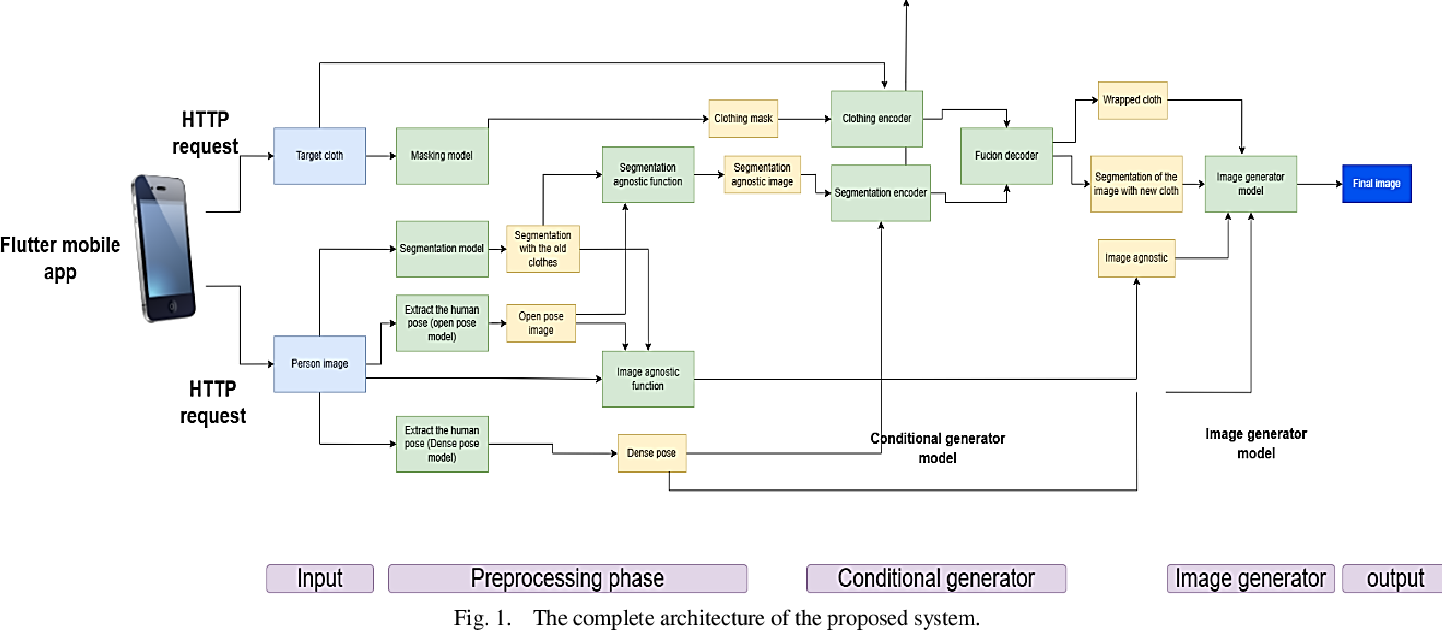
A Cost-Efficient Approach for Creating Virtual Fitting Room using Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
Customers all over the world want to see how the clothes fit them or not before purchasing. Therefore, customers by nature prefer brick-and-mortar clothes shopping so they can try on products before purchasing them. But after the Pandemic of COVID19 many sellers either shifted to online shopping or closed their fitting rooms which made the shopping process hesitant and doubtful. The fact that the clothes may not be suitable for their buyers after purchase led us to think about using new AI technologies to create an online platform or a virtual fitting room (VFR) in the form of a mobile

An IoT Privacy-Oriented selective disclosure credential system
Personal credentials, such as passports and drivers' licenses, can be implemented electronically using multi-show protocols. In this paper, we introduce an IoT Privacy-Oriented selective disclosure credential system, i.e. based on bilinear pairings and multilinear maps. The proposed system consists of three protocols, which allow users to be in control of their personal credentials. The Credentials Authority (CA) verifies and attests to the users credentials. Once the CA signs these credentials, the users cannot modify any of them. Moreover, the users can mask these credentials in every
Anomaly-Based Intrusion Detection for Blackhole Attack Mitigation
In the contemporary environment, mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs) are becoming necessary. They are absolutely vital in a variety of situations where setting up a network quickly is required; however, this is infeasible due to low resources. Ad hoc networks have many applications: education, on the front lines of battle, rescue missions, etc. These networks are distinguished by high mobility and constrained compute, storage, and energy capabilities. As a result of a lack of infrastructure, they do not use communication tools related to infrastructure. Instead, these networks rely on one another
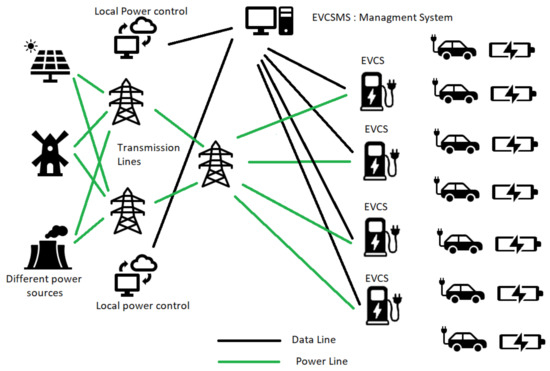
Intrusion Detection for Electric Vehicle Charging Systems (EVCS)
The market for Electric Vehicles (EVs) has expanded tremendously as seen in the recent Conference of the Parties 27 (COP27) held at Sharm El Sheikh, Egypt in November 2022. This needs the creation of an ecosystem that is user-friendly and secure. Internet-connected Electric Vehicle Charging Stations (EVCSs) provide a rich user experience and add-on services. Eventually, the EVCSs are connected to a management system, which is the Electric Vehicle Charging Station Management System (EVCSMS). Attacking the EVCS ecosystem remotely via cyberattacks is rising at the same rate as physical attacks
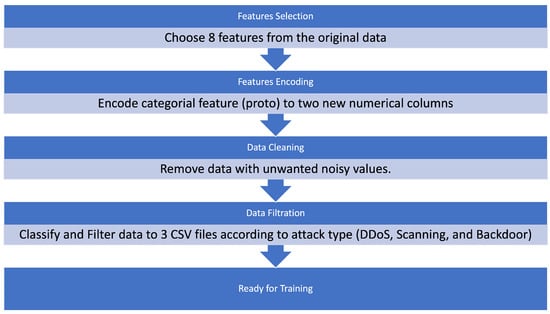
Anomaly Detection of Zero-Day Attacks Based on CNN and Regularization Techniques
The rapid development of cyberattacks in the field of the Internet of things (IoT) introduces new security challenges regarding zero-day attacks. Intrusion-detection systems (IDS) are usually trained on specific attacks to protect the IoT application, but the attacks that are yet unknown for IDS (i.e., zero-day attacks) still represent challenges and concerns regarding users’ data privacy and security in those applications. Anomaly-detection methods usually depend on machine learning (ML)-based methods. Under the ML umbrella are classical ML-based methods, which are known to have low
Study of LiDAR Segmentation and Model’s Uncertainty using Transformer for Different Pre-trainings∗
For the task of semantic segmentation of 2D or 3D inputs, Transformer architecture suffers limitation in the ability of localization because of lacking low-level details. Also for the Transformer to function well, it has to be pre-trained first. Still pre-training the Transformer is an open area of research. In this work, Transformer is integrated into the U-Net architecture as (Chen et al., 2021). The new architecture is trained to conduct semantic segmentation of 2D spherical images generated from projecting the 3D LiDAR point cloud. Such integration allows capturing the the local
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 8
- Next page ››
