Breadcrumb
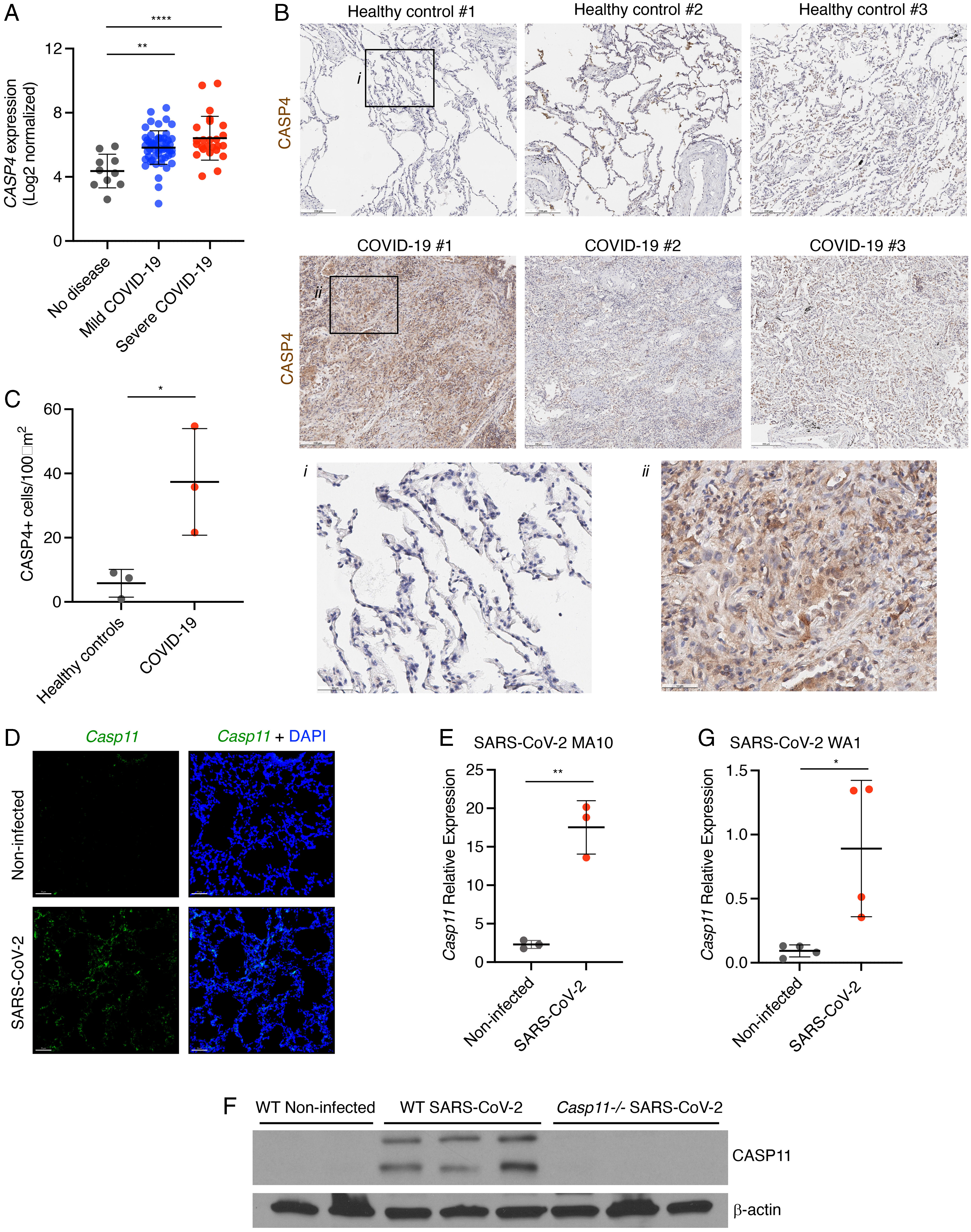
Caspase-4/11 exacerbates disease severity in SARS–CoV-2 infection by promoting inflammation and immunothrombosis
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS–CoV-2) is a worldwide health concern, and new treatment strategies are needed. Targeting inflammatory innate immunity pathways holds therapeutic promise, but effective molecular targets remain elusive. Here, we show that human caspase-4 (CASP4) and its mouse homolog, caspase-11 (CASP11), are up-regulated in SARS–CoV-2 infections and that CASP4 expression correlates with severity of SARS–CoV-2 infection in humans. SARS–CoV-2–infected Casp112/2 mice were protected from severe weight loss and lung pathology, including blood vessel damage
New antileishmanial quinoline linked isatin derivatives targeting DHFR-TS and PTR1: Design, synthesis, and molecular modeling studies
In a search for new drug candidates for one of the neglected tropical diseases, leishmaniasis, twenty quinoline-isatin hybrids were synthesized and tested for their in vitro antileishmanial activity against Leishmania major strain. All the synthesized compounds showed promising in vitro activity against the promastigote form in a low micromolar range (IC50 = 0.5084–5.9486 μM) superior to the reference miltefosine (IC50 = 7.8976 μM). All the target compounds were then tested against the intracellular amastigote form and showed promising inhibition effects (IC50 = 0.60442–8.2948 μM versus 8.08
Multi-omics data integration and analysis pipeline for precision medicine: Systematic review
Precision medicine has gained considerable popularity since the “one-size-fits-all” approach did not seem very effective or reflective of the complexity of the human body. Subsequently, since single-omics does not reflect the complexity of the human body's inner workings, it did not result in the expected advancement in the medical field. Therefore, the multi-omics approach has emerged. The multi-omics approach involves integrating data from different omics technologies, such as DNA sequencing, RNA sequencing, mass spectrometry, and others, using computational methods and then analyzing the
Clay chips and beads capture in situ barley root microbiota and facilitate in vitro long-term preservation of microbial strains
Capturing the diverse microbiota from healthy and/or stress resilient plants for further preservation and transfer to unproductive and pathogen overloaded soils, might be a tool to restore disturbed plant-microbe interactions. Here, we introduce Aswan Pink Clay as a low-cost technology for capturing and storing the living root microbiota. Clay chips were incorporated into the growth milieu of barley plants and developed under gnotobiotic conditions, to capture and host the rhizospheric microbiota. Afterward, it was tested by both a culture-independent (16S rRNA gene metabarcoding) and
In-Silico targeting of SARS-CoV-2 NSP6 for drug and natural products repurposing
Non-Structural Protein 6 (NSP6) has a protecting role for SARS-CoV-2 replication by inhibiting the expansion of autophagosomes inside the cell. NSP6 is involved in the endoplasmic reticulum stress response by binding to Sigma receptor 1 (SR1). Nevertheless, NSP6 crystal structure is not solved yet. Therefore, NSP6 is considered a challenging target in Structure-Based Drug Discovery. Herein, we utilized the high quality NSP6 model built by AlphaFold in our study. Targeting a putative NSP6 binding site is believed to inhibit the SR1-NSP6 protein-protein interactions. Three databases were
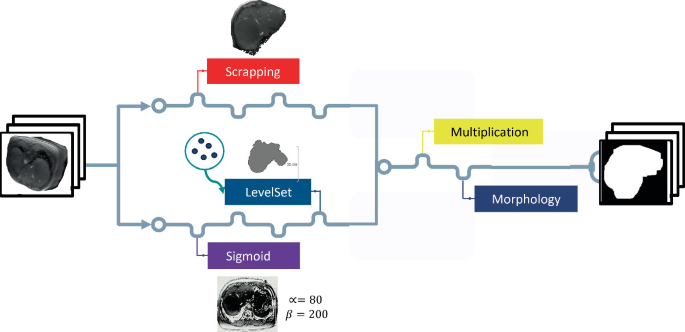
Iterative Refinement Algorithm for Liver Segmentation Ground-Truth Generation Using Fine-Tuning Weak Labels for CT and Structural MRI
Medical image segmentation is indicated in a number of treatments and procedures, such as detecting pathological changes and organ resection. However, it is a time-consuming process when done manually. Automatic segmentation algorithms like deep learning methods overcome this hurdle, but they are data-hungry and require expert ground-truth annotations, which is a limitation, particularly in medical datasets. On the other hand, unannotated medical datasets are easier to come by and can be used in several methods to learn ground-truth masks. In this paper, we aim to utilize across-modalities

ArFakeDetect: A Deep Learning Approach for Detecting Fabricated Arabic Tweets on COVID-19 Vaccines
Social media platforms have emerged as major sources of false information, particularly regarding health topics. like COVID-19 vaccines. This rampant dissemination of inaccurate content contributes significantly to vaccine hesitancy and undermines vaccination campaigns. This research addresses the pressing need for automated methods to distinguish between factual and fabricated Arabic tweets concerning vaccines, aiming to mitigate the spread of misinformation on these platforms. The proposed approach utilizes deep learning techniques, leveraging pre-trained Arabic language models (Arabert)
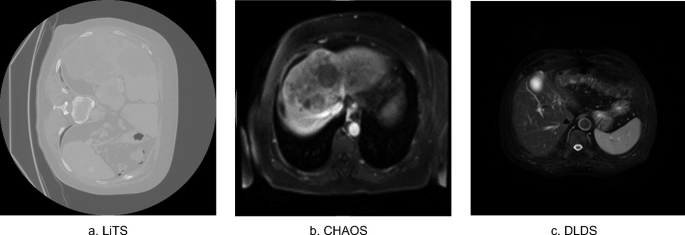
Cross-Modality Deep Transfer Learning: Application to Liver Segmentation in CT and MRI
Liver diseases cause up to two million deaths yearly. Their diagnosis and treatment plans require an accurate assessment of the liver structure and tissue characteristics. Imaging modalities such as computed tomography (CT) and Magnetic resonance (MR) can be used to assess the liver. CT has better spatial resolution compared to MR, which has better tissue contrast. Each modality has its own applications. However, CT is widely used due its ease of access, lower cost and a shorter examination time. Liver segmentation is an important step that helps to accurately identify and isolate the liver
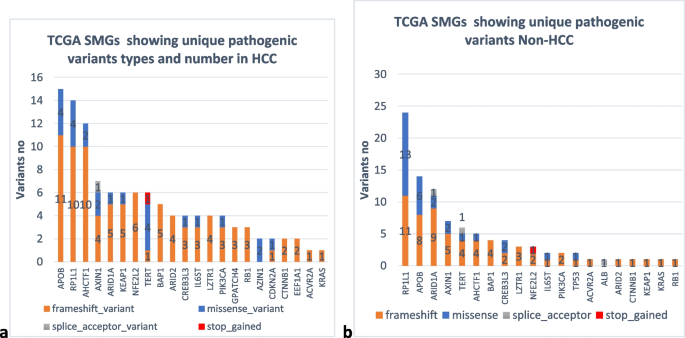
Correction to: Genomic landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma in Egyptian patients by whole exome sequencing (BMC Medical Genomics, (2024), 17, 1, (202), 10.1186/s12920-024-01965-w)
Tables 2, 3, and 6, as shown in the original publication, were modified to black and white during the typesetting process. Following the publication, the authors requested that the tables be reverted to their original-colored versions, as the colors in the heatmap indicate the number of pathogenic variants present in genes. Green indicates the smallest number, and red indicates the highest number. The colored tables are as follows: Heatmap for pathogenic variants in highly mutated genes in HCC samples Heatmap for pathogenic variants in highly mutated genes in Non-HCC samples Heatmap showing
Hybrid Global Optimization Algorithm for Feature Selection
This paper proposes Parallelized Linear Time-Variant Acceleration Coefficients and Inertial Weight of Particle Swarm Optimization algorithm (PLTVACIW-PSO). Its designed has introduced the benefits of Parallel computing into the combined power of TVAC (Time-Variant Acceleration Coefficients) and IW (Inertial Weight). Proposed algorithm has been tested against linear, non-linear, traditional, and multiswarm based optimization algorithms. An experimental study is performed in two stages to assess the proposed PLTVACIW-PSO. Phase I uses 12 recognized Standard Benchmarks methods to evaluate the
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 7
- Next page ››
