Breadcrumb
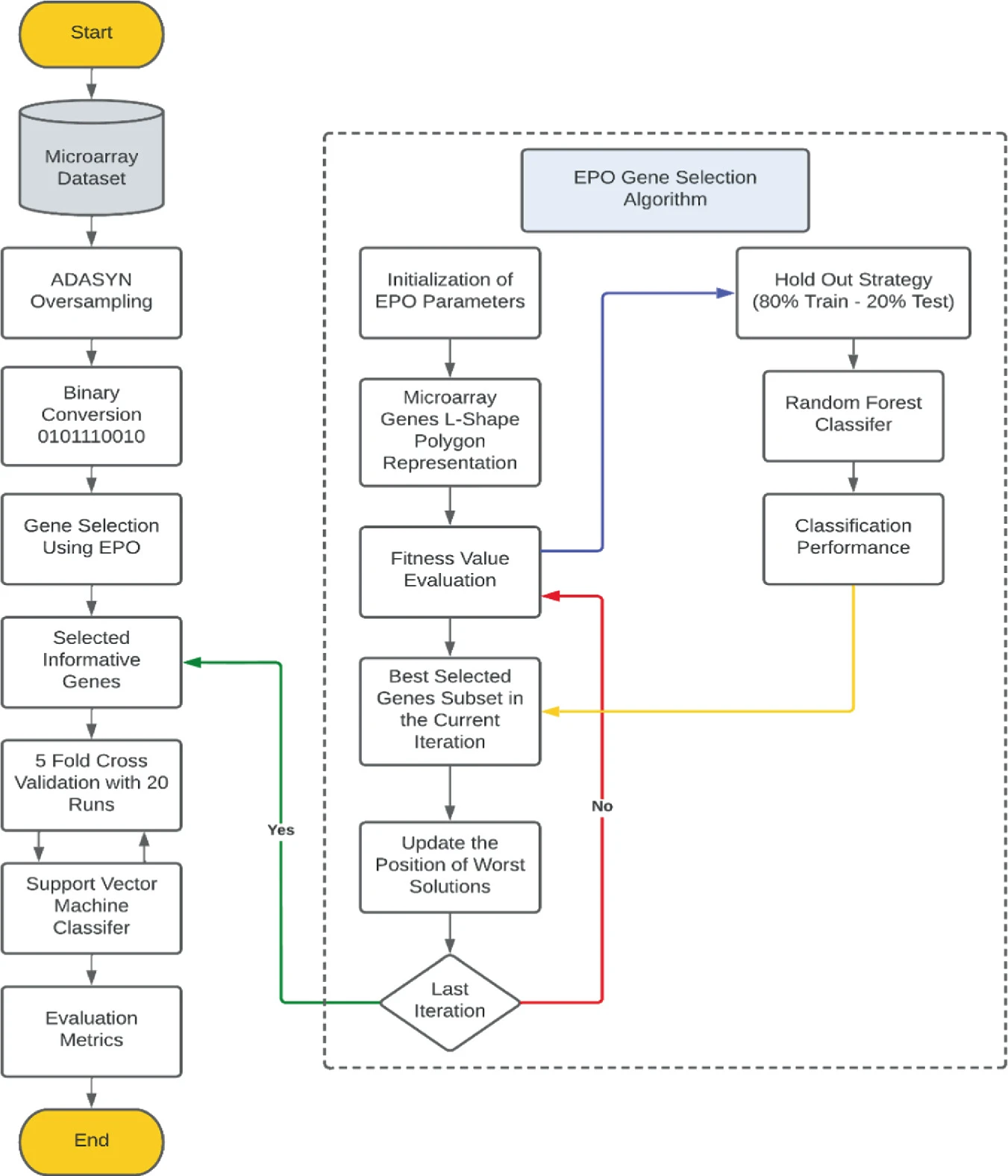
Computational Microarray Gene Selection Model Using Metaheuristic Optimization Algorithm for Imbalanced Microarrays Based on Bagging and Boosting Techniques
Genomic microarray databases encompass complex high dimensional gene expression samples. Imbalanced microarray datasets refer to uneven distribution of genomic samples among different contributed classes which can negatively affect the classification performance. Therefore, gene selection from imbalanced microarray dataset can give rise to misleading, and inconsistent nominated genes that would alter the classification performance. Such unsatisfactory classification performance is due to the skewed distribution of the samples across the microarrays toward the majority class. In this paper, we
Genomic image representation of human coronavirus sequences for COVID-19 detection
Coronavirus (CoV) disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a severe pandemic affecting millions worldwide. Due to its rapid evolution, researchers have been working on developing diagnostic approaches to suppress its spread. This study presents an effective automated approach based on genomic image processing (GIP) techniques to rapidly detect COVID-19, among other human CoV diseases, with high acceptable accuracy. The GIP technique was applied as follows: first, genomic graphical mapping techniques were used to convert the genome sequences into genomic grayscale images. The frequency chaos game

Unravelling Diabetes-related Pathways Using 16S rRNA Microbiome Data from Human Gut and Nasal Cavity
Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) is a complex chronic illness that affects around 90% of diabetic patients worldwide. Prediabetes is an elementary phase for T2D that is recommended to be early diagnosed to prevent its progression. In this study, we used 16S rRNA data from the gut and nasal cavity of prediabetic and control patients to identify common and exclusive diabetic pathways for each body site. Furthermore, using the Phylogenetic Investigation of Communities by Reconstruction of Unobserved States (PICRUSt) as well as MicobiomeExplorer in the pathway enrichment analysis, we also identified the
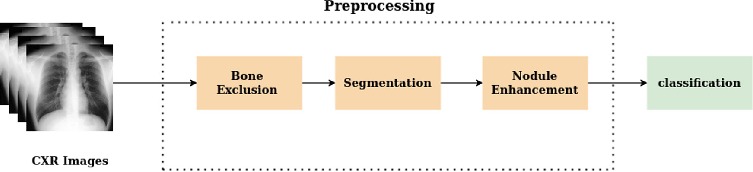
A CAD System for Lung Cancer Detection Using Chest X-ray: A Review
For many years, lung cancer has been ranked among the deadliest illnesses in the world. Therefore, it must be anticipated and detected at an early stage. We need to build a computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) system to help physicians to provide better treatment. In this study, the whole pipeline and the process of the CAD system for lung cancer detection in Chest X-ray are provided. It demonstrates the limitations and the problems facing lung cancer detection. New work is highlighted to be explored by the researchers in this area. Existing studies in the field are reviewed, including their
Arabic English Speech Emotion Recognition System
The Speech Emotion Recognition (SER) system is an approach to identify individuals' emotions. This is important for human-machine interface applications and for the emerging Metaverse. This work presents a bilingual Arabic-English speech emotion recognition system based on EYASE and RAVDESS datasets. A novel feature set was composed by using spectral and prosodic parameters to obtain high performance at a low computational cost. Different classification models were applied. These machine learning classifiers are Random Forest, Support Vector Machine, Logistic Regression, Multi-Layer Perceptron
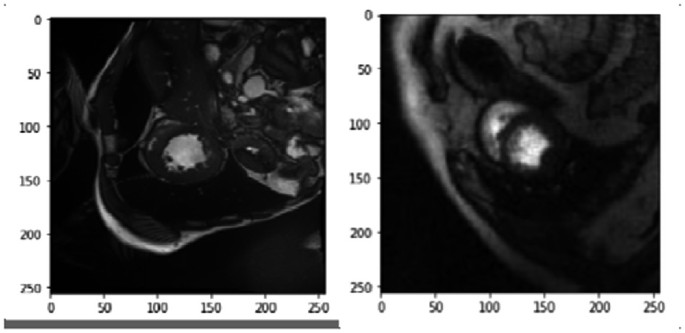
Transfer Learning in Segmenting Myocardium Perfusion Images
Cardiac magnetic resonance perfusion (CMRP) images are used to assess the local function and permeability of the heart muscle. The perfusion analysis requires the segmentation of cardiac inner and outer walls of the left ventricle (LV). However, the available perfusion datasets are limited or have no annotations. A fair dataset was annotated to employ the latest and most effective Deep Learning (DL) methodologies. In this paper, we employ similar cardiac imaging protocols in terms of cardiac geometry by initially training using CINE images and performing domain adaptation to CMRP images using
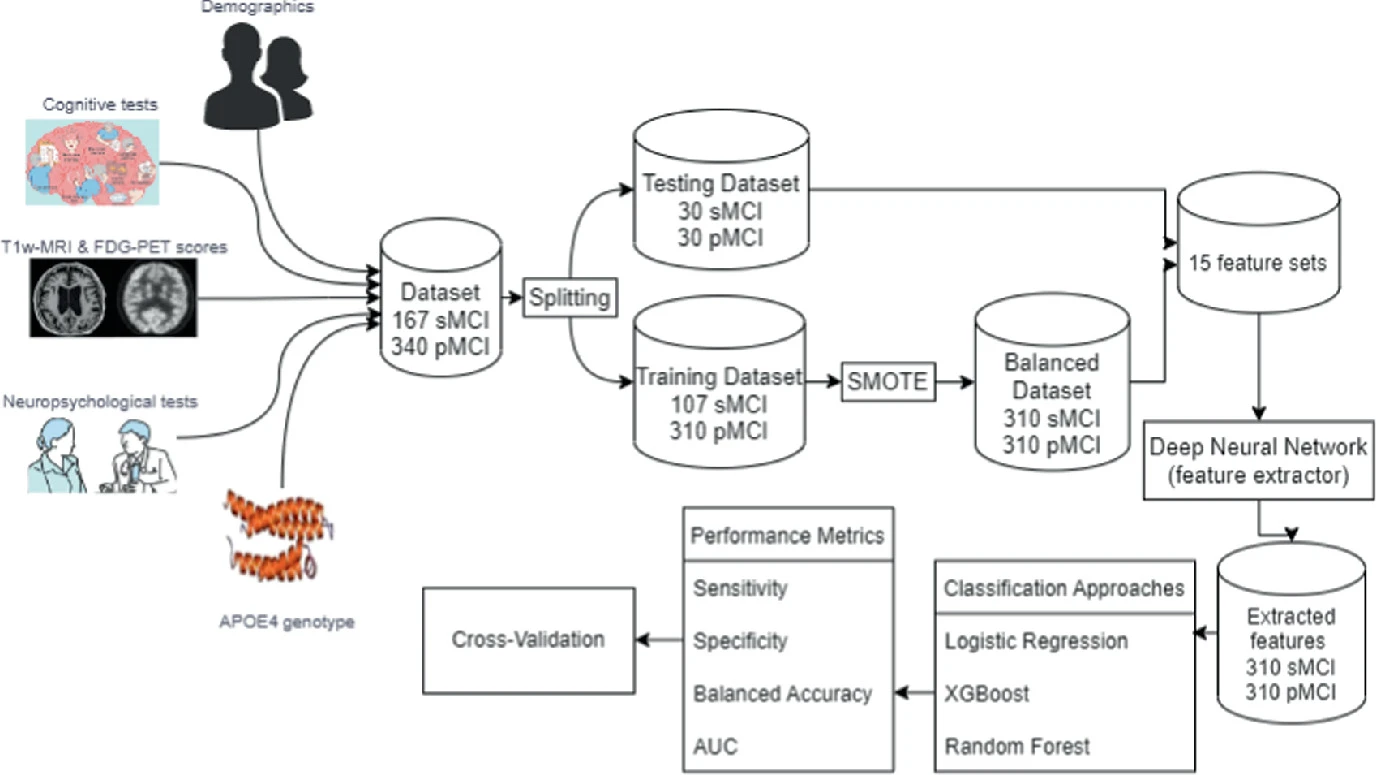
A Novel Diagnostic Model for Early Detection of Alzheimer’s Disease Based on Clinical and Neuroimaging Features
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is a dangerous disease that is known for its characteristics of eroding memory and destroying the brain. The classification of Alzheimer's disease is an important topic that has recently been addressed by many studies using Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL) methods. Most research papers tackling early diagnosis of AD use these methods as a feature extractor for neuroimaging data. In our research paper, the proposed algorithm is to optimize the performance of the prediction of early diagnosis from the multimodal dataset by a multi-step framework that uses a
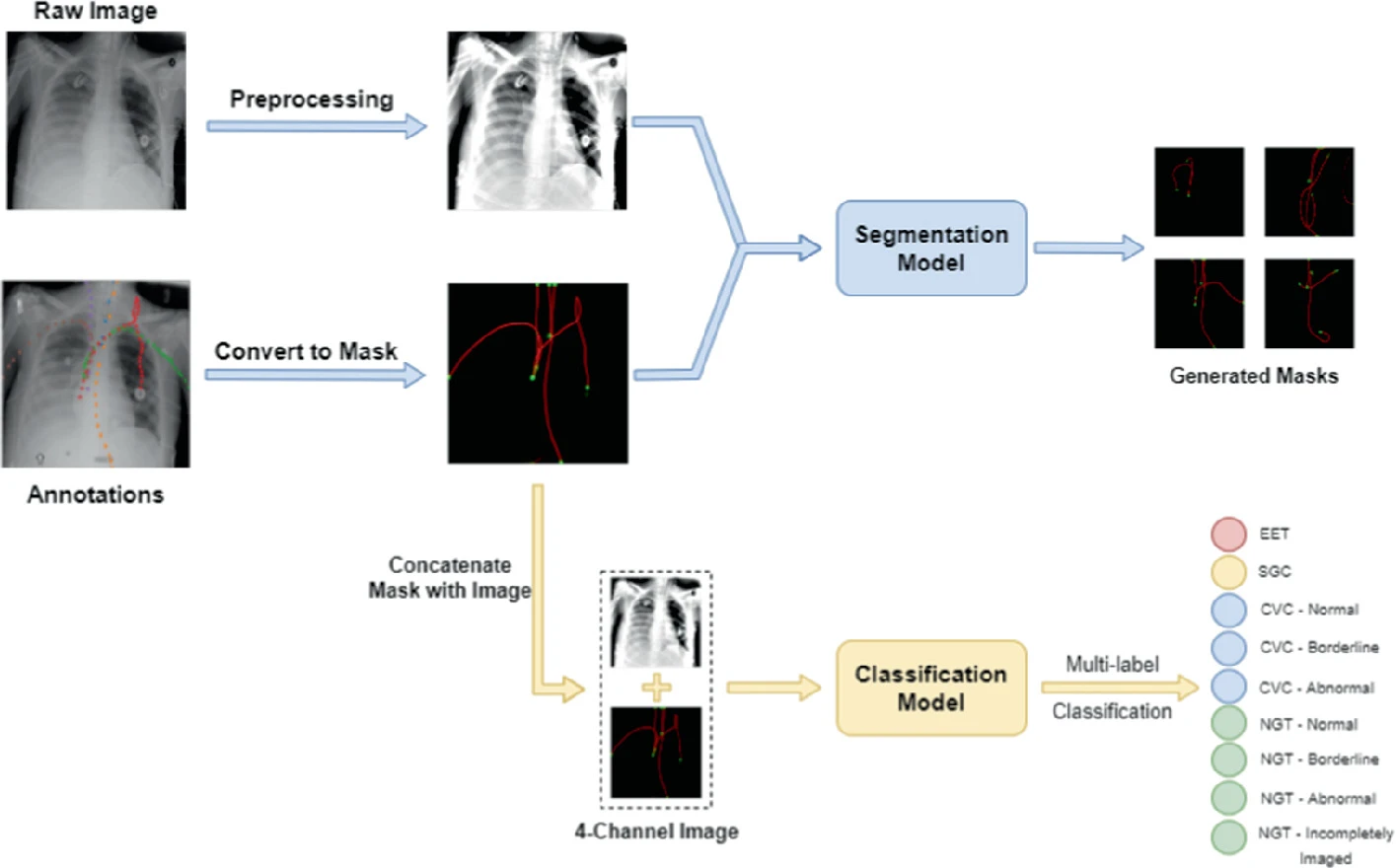
Efficient Pipeline for Rapid Detection of Catheters and Tubes in Chest Radiographs
Catheters are life support devices. Human expertise is often required for the analysis of X-rays in order to achieve the best positioning without misplacement complications. Many hospitals in underprivileged regions around the world lack the sufficient radiology expertise to frequently process X-rays for patients with catheters and tubes. This deficiency may lead to infections, thrombosis, and bleeding due to misplacement of catheters. In the last 2 decades, deep learning has provided solutions to various problems including medical imaging challenges. So instead of depending solely on
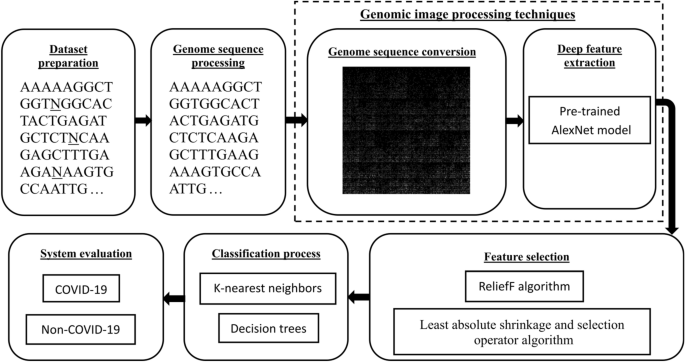
A hybrid deep learning approach for COVID-19 detection based on genomic image processing techniques
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has been spreading quickly, threatening the public health system. Consequently, positive COVID-19 cases must be rapidly detected and treated. Automatic detection systems are essential for controlling the COVID-19 pandemic. Molecular techniques and medical imaging scans are among the most effective approaches for detecting COVID-19. Although these approaches are crucial for controlling the COVID-19 pandemic, they have certain limitations. This study proposes an effective hybrid approach based on genomic image processing (GIP) techniques to
Transcriptomic marker screening for evaluating the mortality rate of pediatric sepsis based on Henry gas solubility optimization
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening medical condition that increases mortality in pediatric populations admitted in the intensive care unit (ICU). Due to the unpredictable nature of the disease course, it was challenging to find the informative genetic biomarkers at the earliest stages. Consequently, a considerable attention has been paid for the early prediction of pediatric sepsis based on genetic biomarkers analysis that would promote the early medical intervention. Therefore, the proposed study attempted to demonstrate the feasibility of Henry Gas Solubility Optimization (HGSO) in
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 3
- Next page ››
