Breadcrumb
New insight into HCV E1/E2 region of genotype 4a
Introduction: Hepatitis C virus (HCV) genome contains two envelope proteins (E1 and E2) responsible for the virus entry into the cell. There is a substantial lack of sequences covering the full length of E1/E2 region for genotype 4. Our study aims at providing new sequences as well as characterizing the genetic divergence of the E1/E2 region of HCV 4a using our new sequences along with all publicly available datasets. Methods: The genomic segments covering the whole E1/E2 region were isolated from Egyptian HCV patients and sequenced. The resulting 36 sequences 36 were analyzed using sequence
Estimation of the myocardium rotation from standard cine Magnetic Resonance Imaging sequences
Myocardium rotation and torsion are important indicators of the cardiac function. Currently, tagged Magnetic Resonance Imaging (tMRI) sequences are analyzed to estimate these parameters. Unfortunately, tMRI is not widely used in clinical practice because it prolongs the scanning time and requires sophisticated analysis software. In this work, we present a method for estimating the myocardium rotation from standard cine MRI sequences. The method is based on identifying special features, i.e. landmarks, of the intensity pattern around the myocardium borders at each timeframe. Each set of
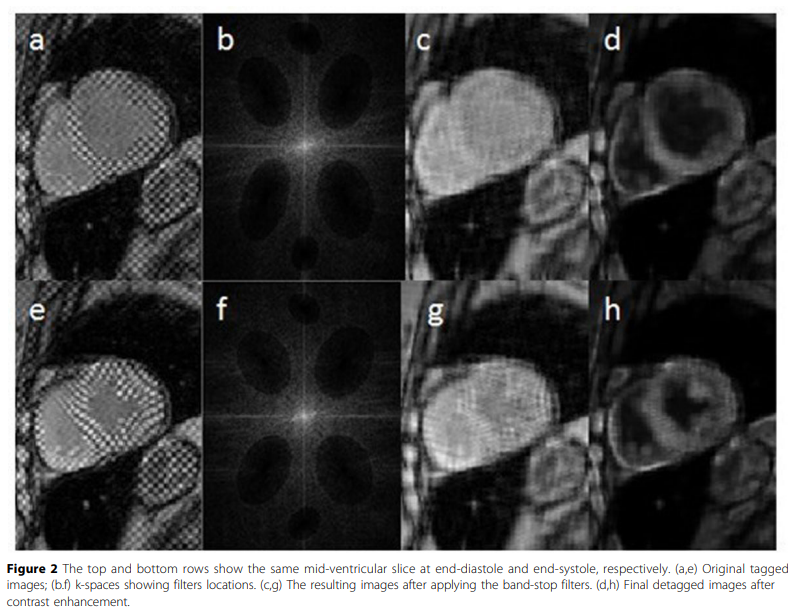
Evaluation of the cardiac global function from tagged magnetic resonance images
Tagged Magnetic Resonance (MR) images are considered the gold standard for evaluating the cardiac regional function. Nevertheless, the low myocardium-to-blood contrast in tagged MR images prevents accurate segmentation of the myocardium, and hence, hinders the quantitative assessment of the global function of the heart. In this work, a method for enhancing the myocardium-to-blood contrast in tagged MR images is proposed. First, the tag pattern in each input tagged MR image is removed using technique based on the image texture and the frequency components of the tag pattern to produce two
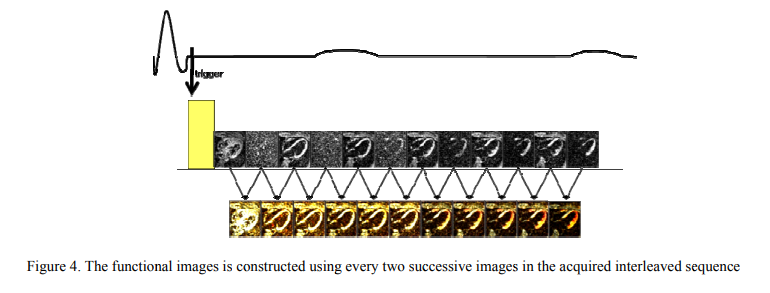
Strain correction in interleaved strain-encoded (SENC) cardiac MR
The strain encoding (SENC) technique directly encodes regional strain of the heart into the acquired MR images and produces two images with two different tunings so that longitudinal strain, on the short-axis view, or circumferential strain on the long-axis view, are measured. Interleaving acquisition is used to shorten the acquisition time of the two tuned images by 50%, but it suffers from errors in the strain calculations due to inter-tunings motion of the heart. In this work, we propose a method to correct for the inter-tunings motion by estimating the motion-induced shift in the spatial
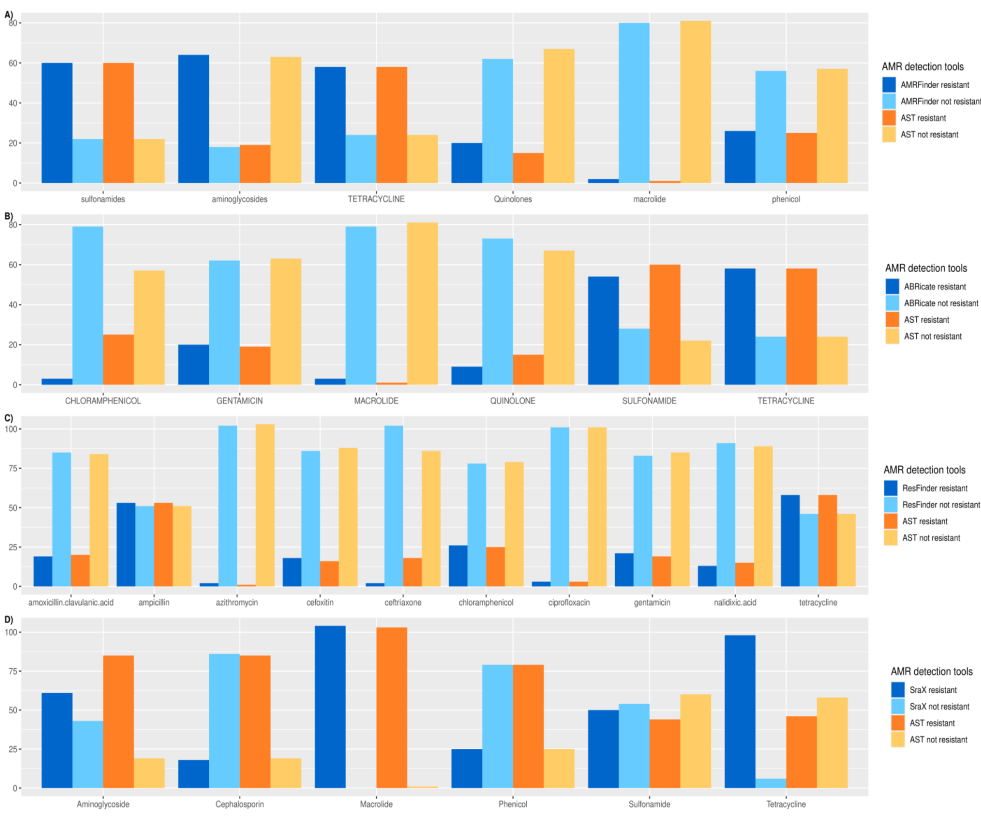
Benchmarking of Antimicrobial Resistance Gene Detection Tools in Assembled Bacterial Whole Genomes
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of the ten dangers threatening our world, according to the world health organization (WHO). Nowadays, there are plenty of electronic microbial genomics and metagenomics data records that represent host-associated microbiomes. These data introduce new insights and a comprehensive understanding of the current antibiotic resistance threats and the upcoming resistance outbreak. Many bioinformatics tools have been developed to detect the AMR genes based on different annotated databases of bacterial whole genome sequences (WGS). The number and structure of
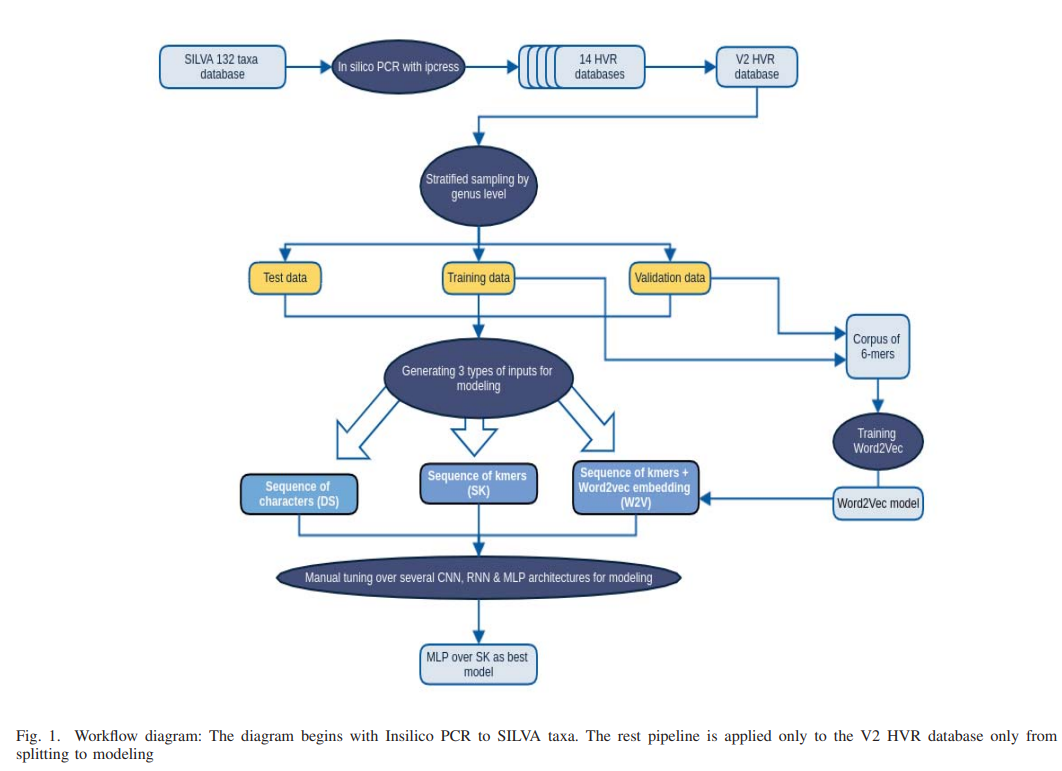
AmpliconNet: Sequence Based Multi-layer Perceptron for Amplicon Read Classification Using Real-time Data Augmentation
Taxonomic assignment is the core of targeted metagenomics approaches that aims to assign sequencing reads to their corresponding taxonomy. Sequence similarity searching and machine learning (ML) are two commonly used approaches for taxonomic assignment based on the 16S rRNA. Similarity based approaches require high computation resources, while ML approaches dont need these resources in prediction. The majority of these ML approaches depend on k-mer frequency rather than direct sequence, which leads to low accuracy on short reads as k-mer frequency doesnt consider k-mer position. Moreover

Ambient and wearable sensing for gait classification in pervasive healthcare environments
Pervasive healthcare environments provide an effective solution for monitoring the wellbeing of the elderly where the general trend of an increasingly ageing population has placed significant burdens on current healthcare systems. An important pervasive healthcare system functionality is patient motion analysis where gait information can be used to detect walking behavior abnormalities that may indicate the onset of adverse health problems, for quantifying post-operative recovery, and to observe the progression of neurodegenerative diseases. The development of accurate motion analysis models
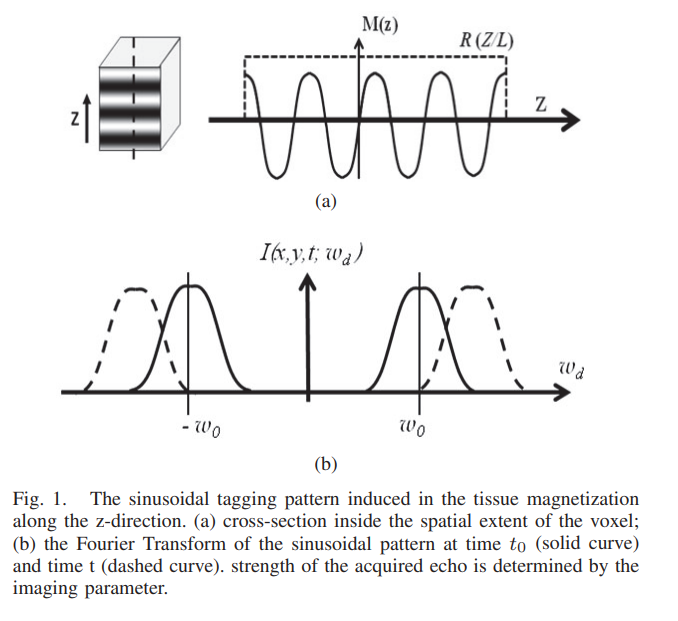
Maximum likelihood estimator for signal intensity in STEAM-based MR imaging techniques
Stimulated echo acquisition mode (STEAM) is a generic imaging technique that lies at the core of many magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques such MRI tagging, displacement encoded MRI, black-blood cardiac imaging. Nevertheless, tissue deformation causes frequency shift of the MR signal and leads to severe signal attenuation. In this work, a maximum likelihood estimator for the signal amplitude is proposed and used to correct the image artifacts. Numerical simulation and real MR data are used to test and validate the proposed method. © 2011 IEEE.
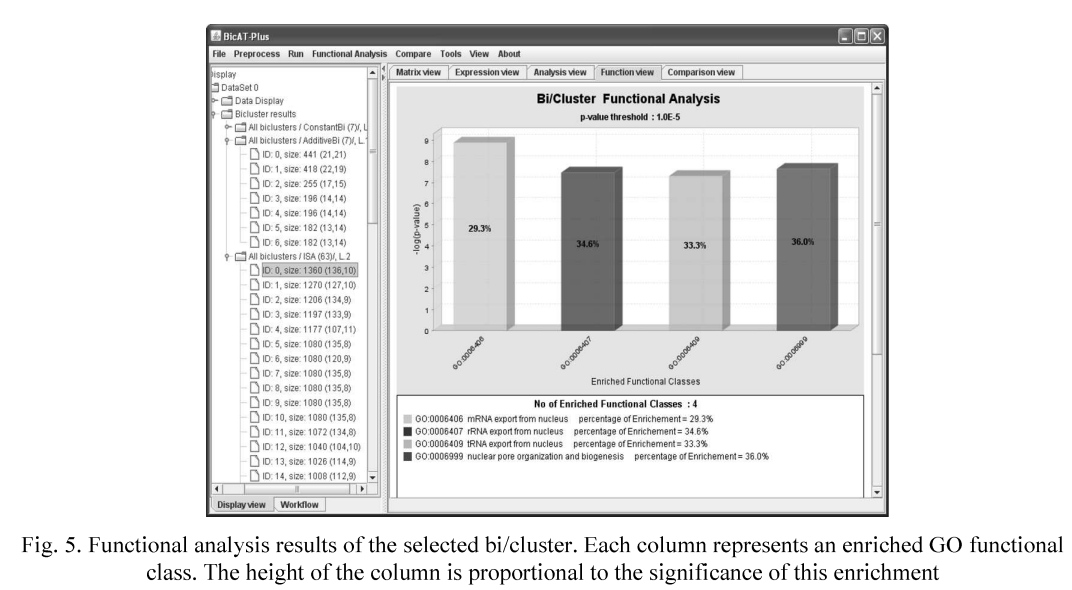
BicATPlus: An automatic comparative tool for Bi/Clustering of gene expression data obtained using microarrays
In the last few years the gene expression microarray technology has become a central tool in the field of functional genomics in which the expression levels of thousands of genes in a biological sample are determined in a single experiment. Several clustering and biclustering methods have been introduced to analyze the gene expression data by identifying the similar patterns and grouping genes into subsets that share biological significance. However, it is not clear how the different methods compare with each other with respect to the biological relevance of the biclusters and clusters as well
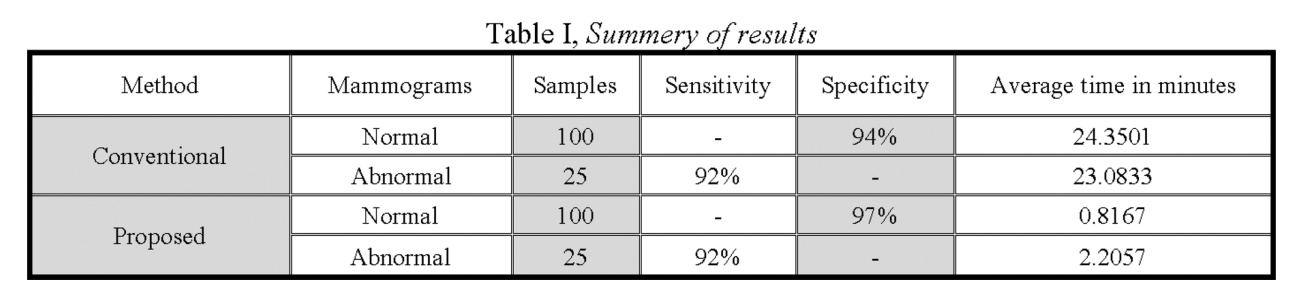
Fast fractal modeling of mammograms for microcalcifications detection
Clusters of microcalcifications in mammograms are an important early sign of breast cancer in women. Comparing with microcalcifications, the breast background tissues have high local self-similarity, which is the basic property of fractal objects. A fast fractal modeling method of mammograms for detecting the presence of microcalcifications is proposed in this paper. The conventional fractal modeling method consumes too much computation time. In the proposed method, the image is divided into shade (homogeneous) and non-shade blocks based on the dynamic range and only the non-shade blocks are
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 14
- Next page ››
