Breadcrumb

OMICS and bioinformatics in Parkinson disease and related movements disorders
This chapter explores the integration of omics and bioinformatics for Parkinson's disease (PD) diagnosis and potential cure discovery. It begins with an overview of PD and its prevalence, followed by an examination of key mutations in genes linked to the disease. These mutations lead to dysfunctional proteins, triggering PD progression. The chapter delves into techniques like whole-exome sequencing (WES), genome-wide association sequencing (GWAS), and whole-genome sequencing (WGS). These methods enable the exploration of omics levels such as lipidomics, metabolomics, genomics, and proteomics
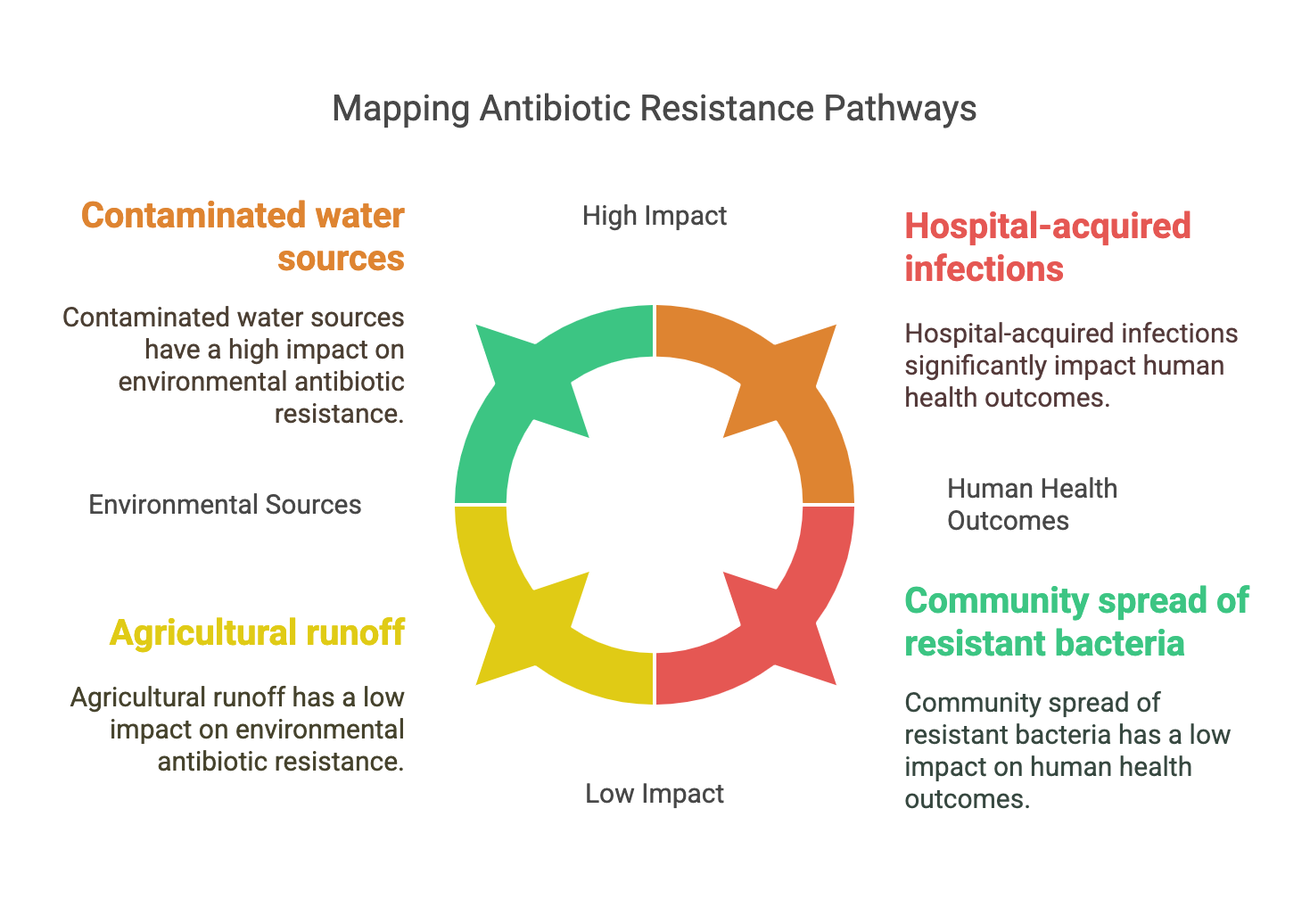
Tracking Antibiotic Resistance from the Environment to Human Health
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is one of the threats to our world according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Resistance is an evolutionary dynamic process where host-associated microbes have to adapt to their stressful environments. AMR could be classified according to the mechanism of resistance or the biome where resistance takes place. Antibiotics are one of the stresses that lead to resistance through antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs). The resistome could be defined as the collection of all ARGs in an organism’s genome or metagenome. Currently, there is a growing body of evidence

Introduction to genomics-based pharmaceutical applications
Biomedical research and pharmaceutical development have been profoundly impacted by genomics in recent years, with researchers gaining new understanding of the genetic pathways underlying disease and opening up new opportunities for the creation of targeted therapeutic interventions. Without a comprehensive grasp of the genetic mechanisms at play, medication discovery approaches in the past often relied on trial and error, targeting particular symptoms or pathways. However, the advent of genomics has changed the game. Scientific advances in high-throughput DNA sequencing have allowed
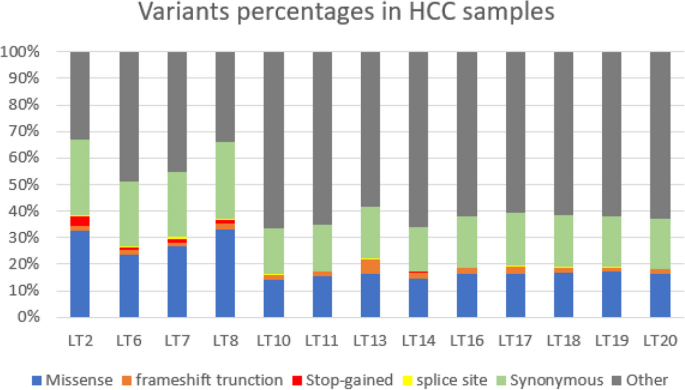
Genomic landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma in Egyptian patients by whole exome sequencing
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary liver cancer. Chronic hepatitis and liver cirrhosis lead to accumulation of genetic alterations driving HCC pathogenesis. This study is designed to explore genomic landscape of HCC in Egyptian patients by whole exome sequencing. Methods: Whole exome sequencing using Ion Torrent was done on 13 HCC patients, who underwent surgical intervention (7 patients underwent living donor liver transplantation (LDLT) and 6 patients had surgical resection}. Results: Mutational signature was mostly S1, S5, S6, and S12 in HCC. Analysis of

Generalisability of fetal ultrasound deep learning models to low-resource imaging settings in five African countries
Most artificial intelligence (AI) research and innovations have concentrated in high-income countries, where imaging data, IT infrastructures and clinical expertise are plentiful. However, slower progress has been made in limited-resource environments where medical imaging is needed. For example, in Sub-Saharan Africa, the rate of perinatal mortality is very high due to limited access to antenatal screening. In these countries, AI models could be implemented to help clinicians acquire fetal ultrasound planes for the diagnosis of fetal abnormalities. So far, deep learning models have been
Oral Dental Diagnosis Using Deep Learning Techniques: A Review
The purpose of this study is to investigate the gradual incorporation of deep learning in the dental healthcare system, offering an easy and efficient diagnosis. For that, an electronic search was conducted in the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Xplore, ScienceDirect, Journal of Dentistry, Health Informatics Journal, and other credible resources. The studies varied with their tools and techniques used for the diagnosis while coping with the rapid deep-learning evolving base, with different types of conducting tools and analysis for the data. An inclusion criterion was
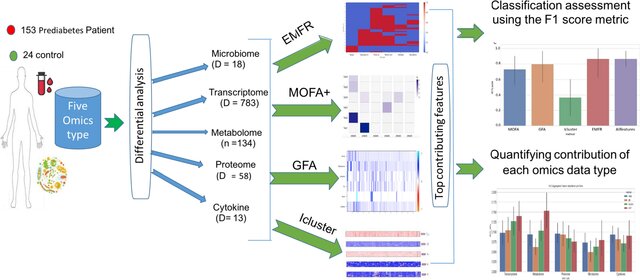
Comparative evaluation of multiomics integration tools for the study of prediabetes: insights into the earliest stages of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D) remains a critical health concern, particularly in its early disease stages such as prediabetes. Understanding these early stages is paramount for improving patient outcomes. Multiomics data integration tools offer promise in unraveling the underlying mechanisms of T2D. The advent of high-throughput technology and the increasing availability of multiomics data has led to the development of several statistical and network-based integration methods. However, the performance of such methods varies, requiring their output evaluation in an unbiased manner. Here, we
Smart Prediction of Circulatory Failure: Machine Learning for Early Detection of Patient Deterioration
Circulatory failure, also known as shock, is a critical condition that can have serious consequences for one's health. Early detection and timely intervention are crucial for improving patient outcomes. Machine learning (ML) models have shown promise in predicting circulatory failure based on clinical data. In our study, we examined different machine learning (ML) models to predict circulatory failure in patients who were admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) with suspected circulatory problems. The ML model we developed used various algorithms like random forest, LG, XGB, Decision Tree
Hybrid Global Optimization Algorithm for Feature Selection
This paper proposes Parallelized Linear Time-Variant Acceleration Coefficients and Inertial Weight of Particle Swarm Optimization algorithm (PLTVACIW-PSO). Its designed has introduced the benefits of Parallel computing into the combined power of TVAC (Time-Variant Acceleration Coefficients) and IW (Inertial Weight). Proposed algorithm has been tested against linear, non-linear, traditional, and multiswarm based optimization algorithms. An experimental study is performed in two stages to assess the proposed PLTVACIW-PSO. Phase I uses 12 recognized Standard Benchmarks methods to evaluate the
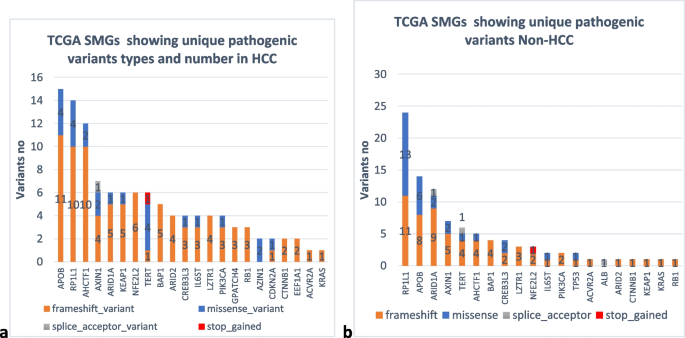
Correction to: Genomic landscape of hepatocellular carcinoma in Egyptian patients by whole exome sequencing (BMC Medical Genomics, (2024), 17, 1, (202), 10.1186/s12920-024-01965-w)
Tables 2, 3, and 6, as shown in the original publication, were modified to black and white during the typesetting process. Following the publication, the authors requested that the tables be reverted to their original-colored versions, as the colors in the heatmap indicate the number of pathogenic variants present in genes. Green indicates the smallest number, and red indicates the highest number. The colored tables are as follows: Heatmap for pathogenic variants in highly mutated genes in HCC samples Heatmap for pathogenic variants in highly mutated genes in Non-HCC samples Heatmap showing
Pagination
- Page 1
- Next page ››
