Breadcrumb

Uni-Buddy: A Multifunctional AI-Powered Assistant for Enhancing University Life: A Use Case at Nile University
Uni-Buddy is an advanced AI system developed to simplify university life at Nile University. It efficiently handles questions in everyday language, accesses real-time university databases, and simultaneously provides accurate responses for multiple users. Its goals include assisting with course registration, academic advising, financial inquiries, campus navigation, and research support. The evaluation demonstrates Uni-Buddy's user-friendly design, effective navigation, language comprehension, and database connectivity proficiency. Compared to similar studies, it stands out for its ease of use

Unravelling Diabetes-related Pathways Using 16S rRNA Microbiome Data from Human Gut and Nasal Cavity
Type 2 Diabetes (T2D) is a complex chronic illness that affects around 90% of diabetic patients worldwide. Prediabetes is an elementary phase for T2D that is recommended to be early diagnosed to prevent its progression. In this study, we used 16S rRNA data from the gut and nasal cavity of prediabetic and control patients to identify common and exclusive diabetic pathways for each body site. Furthermore, using the Phylogenetic Investigation of Communities by Reconstruction of Unobserved States (PICRUSt) as well as MicobiomeExplorer in the pathway enrichment analysis, we also identified the
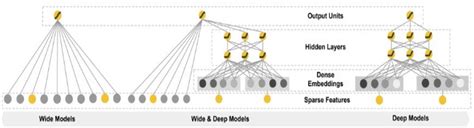
Using graph embeddings to improve the performance of embedding based recommender Systems
This paper discusses the use of node2vec graph embeddings to improve the performance of wide and deep recommenders by substituting the embedding layer with graph embeddings to leverage its representational power without major investments in migrating from current recommender systems. First, recommender systems importance in modern day platforms is discussed. Then, the magnitude of investment needed to deploy a recommender system into a production environment is discussed and finally, wide and deep recommenders and their importance in industry is outlined along with our experiments and results
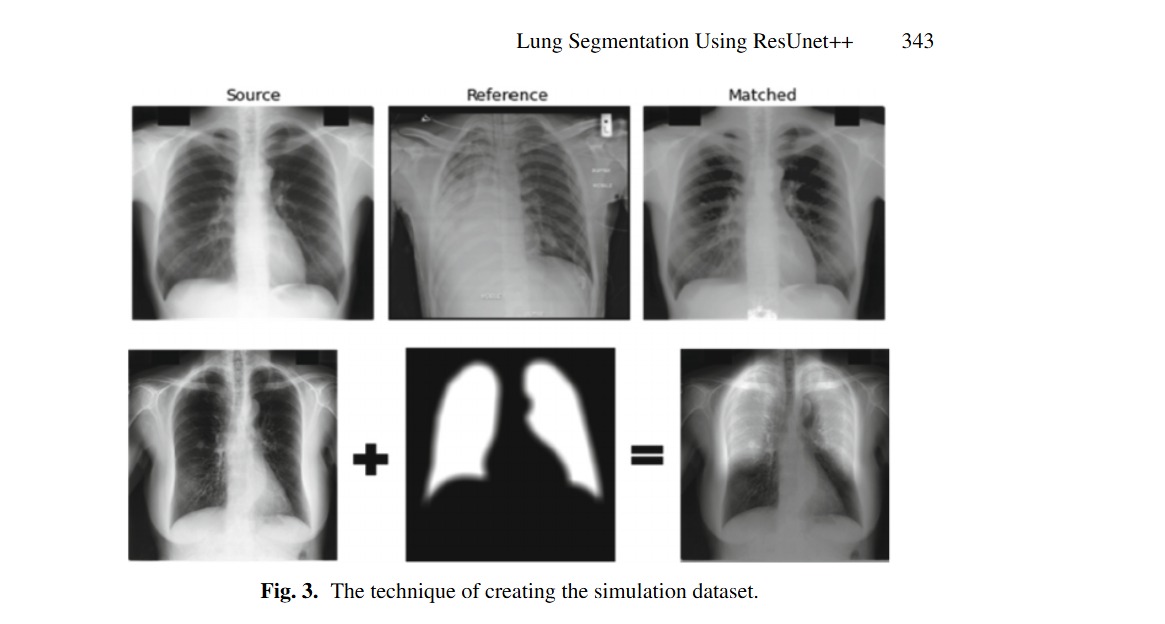
Lung Segmentation Using ResUnet++ Powered by Variational Auto Encoder-Based Enhancement in Chest X-ray Images
X-ray has a huge popularity around the world. This is due to its low cost and easy to access. Most of lung diseases are diagnosed using Chest X-ray (CXR). So, developing computer aided detection (CAD) provided with automatic lung segmentation can improve the efficiency of the detection and support the physicians to make a reliable decision at early stages. But when the input image has image artifacts, then any lung segmentation model will introduce suboptimal lung segmentation results. In this paper, a new approach is proposed to make the lung segmentation model robust and boost the basic
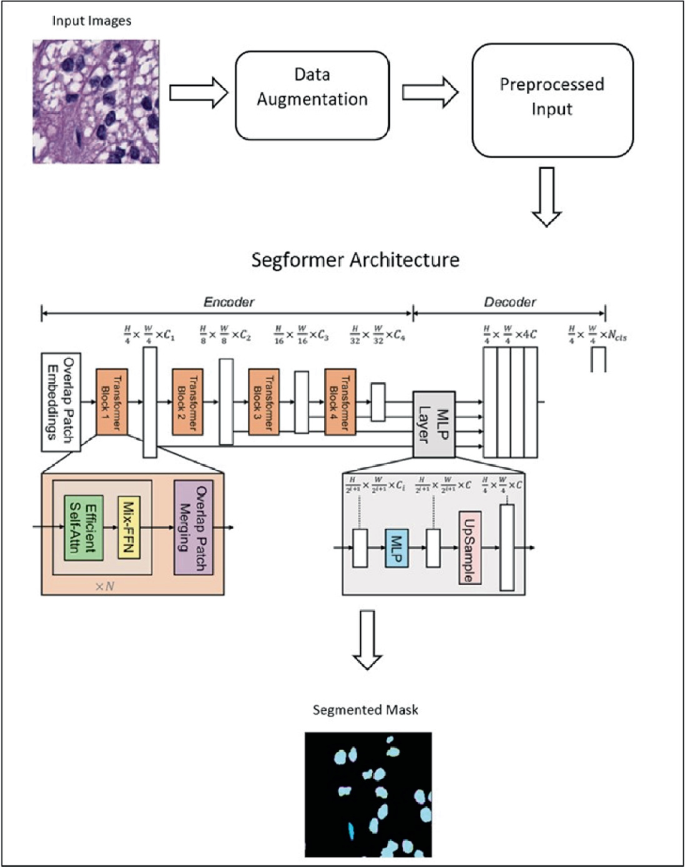
Efficient Semantic Segmentation of Nuclei in Histopathology Images Using Segformer
Segmentation of nuclei in histopathology images with high accuracy is crucial for the diagnosis and prognosis of cancer and other diseases. Using Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the segmentation process enables pathologists to identify and study the unique properties of individual cells, which can reveal important information about the disease, its stage, and the best treatment approach. By using AI-powered automatic segmentation, this process can be significantly improved in terms of efficiency and accuracy, resulting in faster and more precise diagnoses. Ultimately, this can potentially lead

A Review of the Role of ChatGPT for Clinical Decision Support Systems
The development of artificial intelligence (AI) provided powerful assistant tools for humans in various aspects. Healthcare is rapidly evolving, with AI playing a crucial role in improving patient care. The extensive use of AI in Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) enables providing real-time evidence-based recommendations to healthcare professionals at the point of Care. The AI chatbot ChatGPT proved its ability to solve several natural language processing tasks. One notable advancement is the integration of ChatGPT into Clinical Decision Support Systems. ChatGPT, despite not being

Detecting Mimikatz in Lateral Movements Using Windows API Call Sequence Analysis
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) is classified as a high threat stealthy attack on modern networks. It uses sophisticated techniques, which makes it very challenging to be detected. It can remain undetectable for an extended period by gaining unauthorized access and lateral movements in the target network. Depending on the APT group tools, responding to the initiated attack can be challenging and composite. Mimikatz is a credential theft tool used in many APT attacks to achieve their objectives. It calls Windows APIs in a particular order during the execution time. This makes the APT group

Evaluating the Performance of Lightweight Block Ciphers for Resource-Constrained IoT Devices
In the context of the Internet of Things (IoT), lightweight block ciphers are of vital importance. Due to the nature of the devices involved, traditional security solutions can add overhead and perhaps inhibit the application's objective due to resource limits. Lightweight cryptography is a novel suite of ciphers that aims to provide hardware-constrained devices with a high level of security while maintaining a low physical cost and high performance. In this paper, we are going to evaluate the performance of some of the recently proposed lightweight block ciphers (GIFT-COFB, Romulus, and
Autonomous Traffic-Aware and QoS-Constrained Capacity Cell Shutdown for Green Mobile Networks
Energy efficiency of Radio Access Networks (RANs) is increasingly becoming a global strategic priority for Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) and governments to attain sustainable and uninterruptible network services. In this work, we propose an autonomous Machine Learning (ML)-based framework to maximize RAN energy efficiency via underutilized radio resource shutdown while maintaining an adequate network capacity with a preset Quality-Of-Service (QoS) level. This is achieved by dynamically switching radio resources on and off according to service demand. Training on a live network dataset and

Dynamic Modeling and Identification of the COVID-19 Stochastic Dispersion
In this work, the stochastic dispersion of novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) at the borders between France and Italy has been considered using a multi-input multi-output stochastic model. The physical effects of wind, temperature and altitude have been investigated as these factors and physical relationships are stochastic in nature. Stochastic terms have also been included to take into account the turbulence effect, and the r and om nature of the above physical parameters considered. Then, a method is proposed to identify the developed model's order and parameters. The actual data has
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 2
- Next page ››
