Breadcrumb
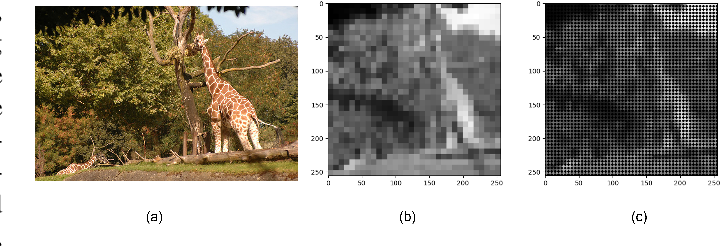
Enhancing Scene Simplification and Optimization for Retinal Prosthesis Platform
Retinal prostheses are designed to aid individuals with retinal degenerative conditions such as Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP) and Age-related Macular Degeneration (AMD). These prostheses seek to restore vision and improve the perceived scene by stimulating degenerated retinal cells using retinal stimulating electrodes. While these electrodes allow more efficient interaction with the surroundings, they offer limited resolution.This paper presents an innovative approach to revolutionize the visual perception of retinal prosthesis users. The key idea behind the proposed approach is to fuse
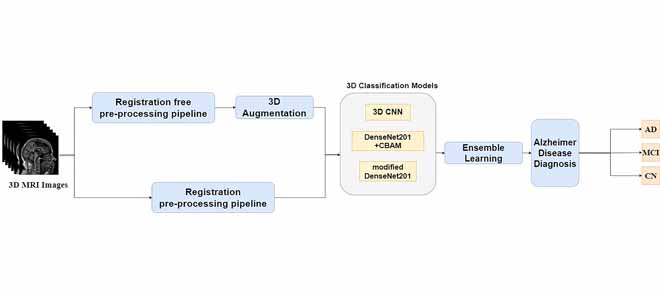
Automatic Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease Using 3D Deep Ensemble Approach
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is considered the 6 th leading cause of death worldwide. Early diagnosis of AD is not an easy task, and no preventive cures have been discovered yet. Having an accurate computer-aided system for the early detection of AD is important to help patients with AD. This study proposes a new approach for classifying disease stages. First, we worked on the MRI images and split them into an appropriate format to avoid data leakage. Subsequently, a simple and fast registration-free preprocessing pipeline was applied to the dataset. Numerous experiments were conducted to analyze
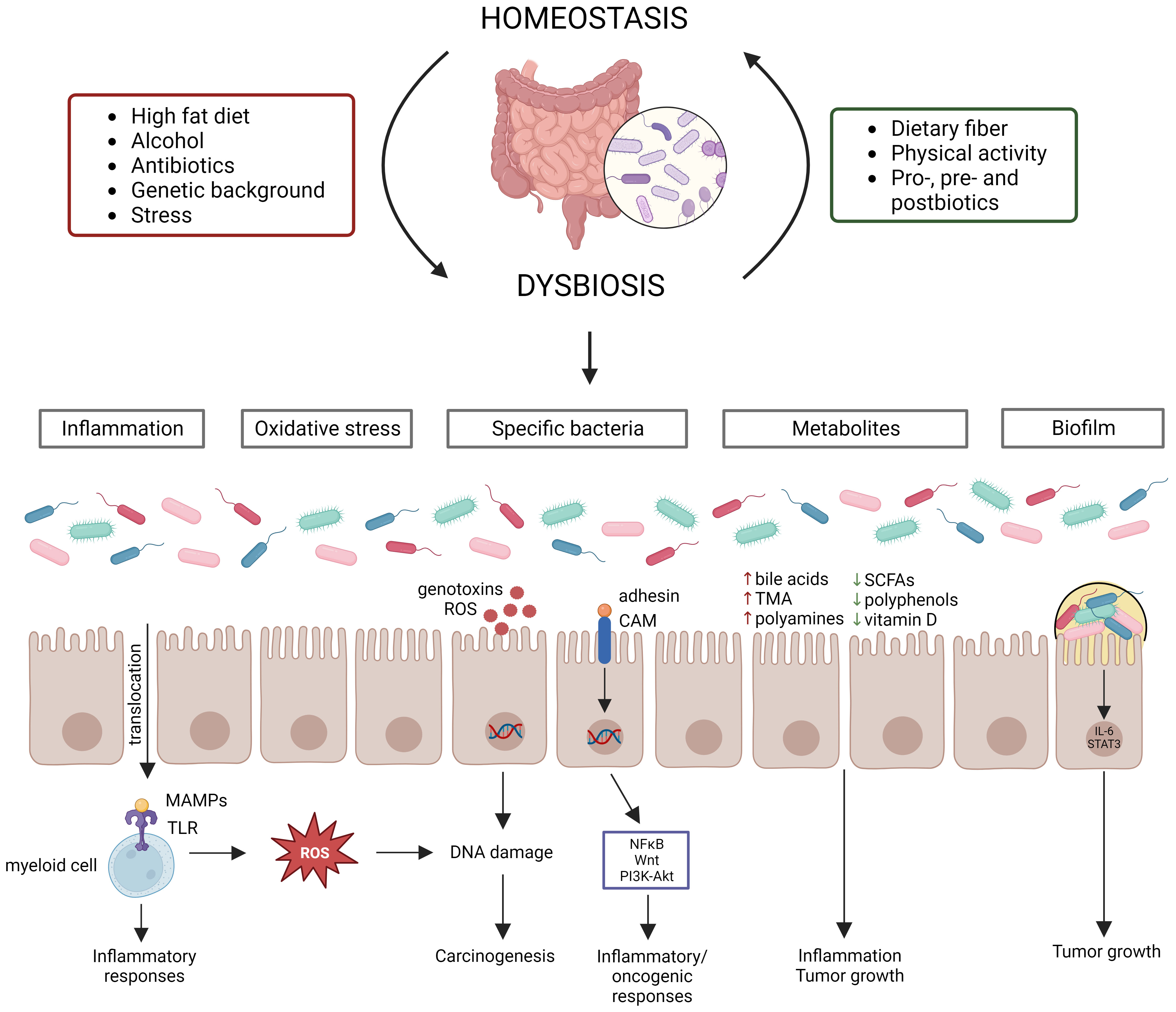
Dissecting the role of the gut microbiome and fecal microbiota transplantation in radio- and immunotherapy treatment of colorectal cancer
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most commonly diagnosed cancers and poses a major burden on the human health worldwide. At the moment, treatment of CRC consists of surgery in combination with (neo)adjuvant chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy. More recently, immune checkpoint blockers (ICBs) have also been approved for CRC treatment. In addition, recent studies have shown that radiotherapy and ICBs act synergistically, with radiotherapy stimulating the immune system that is activated by ICBs. However, both treatments are also associated with severe toxicity and efficacy issues, which can

A Review of the Role of ChatGPT for Clinical Decision Support Systems
The development of artificial intelligence (AI) provided powerful assistant tools for humans in various aspects. Healthcare is rapidly evolving, with AI playing a crucial role in improving patient care. The extensive use of AI in Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) enables providing real-time evidence-based recommendations to healthcare professionals at the point of Care. The AI chatbot ChatGPT proved its ability to solve several natural language processing tasks. One notable advancement is the integration of ChatGPT into Clinical Decision Support Systems. ChatGPT, despite not being

Detecting Mimikatz in Lateral Movements Using Windows API Call Sequence Analysis
Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) is classified as a high threat stealthy attack on modern networks. It uses sophisticated techniques, which makes it very challenging to be detected. It can remain undetectable for an extended period by gaining unauthorized access and lateral movements in the target network. Depending on the APT group tools, responding to the initiated attack can be challenging and composite. Mimikatz is a credential theft tool used in many APT attacks to achieve their objectives. It calls Windows APIs in a particular order during the execution time. This makes the APT group

Evaluating the Performance of Lightweight Block Ciphers for Resource-Constrained IoT Devices
In the context of the Internet of Things (IoT), lightweight block ciphers are of vital importance. Due to the nature of the devices involved, traditional security solutions can add overhead and perhaps inhibit the application's objective due to resource limits. Lightweight cryptography is a novel suite of ciphers that aims to provide hardware-constrained devices with a high level of security while maintaining a low physical cost and high performance. In this paper, we are going to evaluate the performance of some of the recently proposed lightweight block ciphers (GIFT-COFB, Romulus, and
Autonomous Traffic-Aware and QoS-Constrained Capacity Cell Shutdown for Green Mobile Networks
Energy efficiency of Radio Access Networks (RANs) is increasingly becoming a global strategic priority for Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) and governments to attain sustainable and uninterruptible network services. In this work, we propose an autonomous Machine Learning (ML)-based framework to maximize RAN energy efficiency via underutilized radio resource shutdown while maintaining an adequate network capacity with a preset Quality-Of-Service (QoS) level. This is achieved by dynamically switching radio resources on and off according to service demand. Training on a live network dataset and

Dynamic Modeling and Identification of the COVID-19 Stochastic Dispersion
In this work, the stochastic dispersion of novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) at the borders between France and Italy has been considered using a multi-input multi-output stochastic model. The physical effects of wind, temperature and altitude have been investigated as these factors and physical relationships are stochastic in nature. Stochastic terms have also been included to take into account the turbulence effect, and the r and om nature of the above physical parameters considered. Then, a method is proposed to identify the developed model's order and parameters. The actual data has

Diabetic Retinopathy Detection: A PySpark-Driven Approach with VGG 16 Feature Extraction and MLP Classification
The current study used cutting-edge techniques to experimentally test the early diagnosis of diabetes via retinal scans. The goal was to enable effective disease prediction and management by facilitating quick and precise medical diagnostics. Three processes were involved in the development of a Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) diagnosis tool: feature extraction, feature reduction, and image classification. The research employed Apache Spark, a distributed computing framework, to manage large datasets and enhance the performance of the multilayer perceptron (MLP) model via hyperparameter tuning and
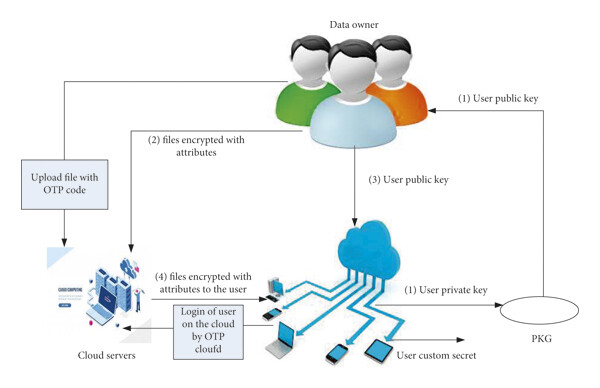
A New Secure Model for Data Protection over Cloud Computing
The main goal of any data storage model on the cloud is accessing data in an easy way without risking its security. A security consideration is a major aspect in any cloud data storage model to provide safety and efficiency. In this paper, we propose a secure data protection model over the cloud. The proposed model presents a solution to some security issues of cloud such as data protection from any violations and protection from a fake authorized identity user, which adversely affects the security of the cloud. This paper includes multiple issues and challenges with cloud computing that
Pagination
- Previous page ‹‹
- Page 8
- Next page ››
